Heres How To Plow Some Of Your Profits Into Retirement Savings
Eric is currently a duly licensed Independent Insurance Broker licensed in Life, Health, Property, and Casualty insurance. He has worked more than 13 years in both public and private accounting jobs and more than four years licensed as an insurance producer. His background in tax accounting has served as a solid base supporting his current book of business.
Just because you are a one-person outfit, a freelancer, or an independent contractor doesnât mean you have to do without a retirement savings plan or the tax benefits that accompany them.
One option If you are self-employed is the solo 401, also known as an independent 401 plan. In fact, the Solo 401 has some benefits over other types of retirement accounts available to the self-employed.
Withdrawing Funds From A Self
As with traditional 401 plans, the self-employed 401 is intended to help you save money for retirement, and there are regulations in place to encourage you to do so. For example:
- Withdrawals prior to age 59½ may be subject to a 10% early withdrawal penalty, along with any applicable income taxes1
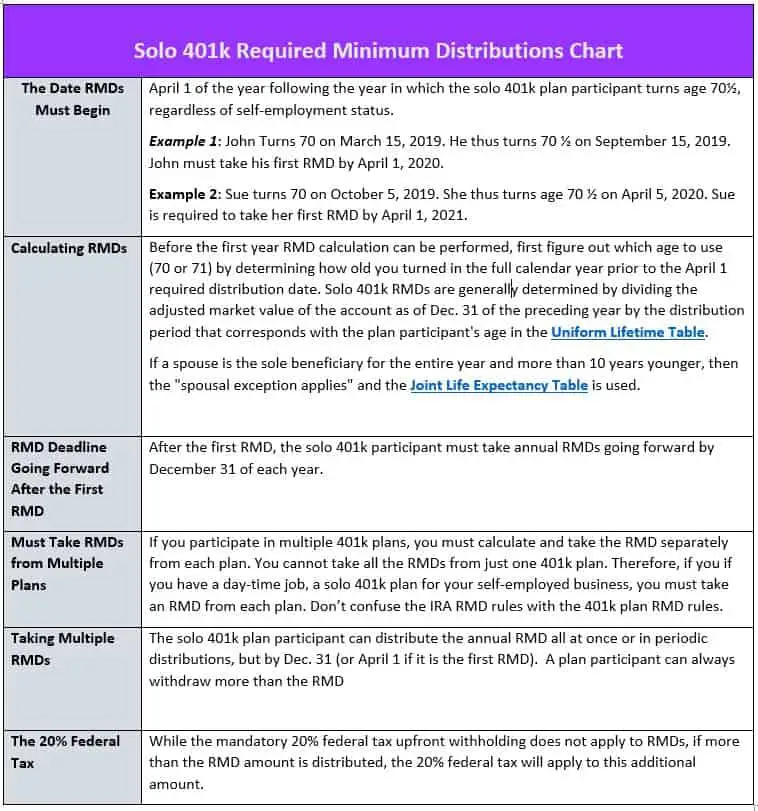
- You must take required minimum distributions from self-employed 401s beginning at age 722
- Plans can be structured to allow loans or hardship distributions3
- Plans can be structured to accept rollovers from other retirement accounts, including SEP IRAs and traditional 401s, into your self-employed 401
- You can roll your self-employed 401 assets into another 401 or an IRA
Because of its high contribution levels, flexible investment options, and relatively easy administration, the self-employed 401 is an attractive option for small-business owners or sole proprietors who want to be able to save aggressively for the future.
If there is the potential that your business might add employees at a later date, however, know that you will either have to convert your self-employed 401 plan to a traditional 401, or else terminate it. But if you’re confident that you will remain a one-person operation, and you want the high savings options that these plans offer, this type of account may be a good fit.
Solo 401 Contribution Limits
The total solo 401 contribution limit is up to $58,000 in 2021 and $61,000 in 2022. There is a catch-up contribution of an extra $6,500 for those 50 or older.
To understand solo 401 contribution rules, you want to think of yourself as two people: an employer and an employee . Within that overall $58,000 contribution limit in 2021 and $61,000 in 2022, your contributions are subject to additional limits in each role:
-
As the employee, you can contribute up to $19,500 in 2021 and $20,500 in 2022, or 100% of compensation, whichever is less. Those 50 or older get to contribute an additional $6,500 here.
-
As the employer, you can make an additional profit-sharing contribution of up to 25% of your compensation or net self-employment income, which is your net profit less half your self-employment tax and the plan contributions you made for yourself. The limit on compensation that can be used to factor your contribution is $290,000 in 2021 and $305,000 in 2022.
Keep in mind that if youre side-gigging, employee 401 limits apply by person, rather than by plan. That means if youre also participating in a 401 at your day job, the limit applies to contributions across all plans, not each individual plan.
Read Also: When Do Sole Treadmills Go On Sale
Recommended Reading: How To Start Withdrawing From 401k
You May Qualify For A Solo 401 If You Are Self
Solo 401s are available for owners and operators of:
- Sole proprietorships
Many types of people are considered self-employed:
- Adult Care Providers
- Writers and Editors
Self-employment can be part-time, and it can coexist with full-time employment elsewhere. If you participate in an employers 401, you may still have your own Solo 401, but you are only able to contribute a maximum of $20,500 total to your accounts as employee. Having your own Solo 401 will allow you to contribute an extra $40,500 or $47,000 as an employer.
Get Your Complimentary Guide to Solo 401 plans
How Do I Know If I Qualify For A Solo 401 Plan
A solo 401 is an individual 401 designed for a business owner with no employees. Empower your future with Ubiquity’s Single® plan:
- Invest in a wide range of investment options through a self directed brokerage account at any financial institution of your choice
- Reduce your taxable income with Traditional or Roth options
- Get access to funds through a loan option
If youre an entrepreneur, a Solo 401 plan is a smart money move to increase your wealth, reduce your tax burden, and secure your retirement.
Recommended Reading: Do I Need To Rollover My 401k To New Employer
Naming The Solo 401k Question
Th name of the self-employed business will not impact the Solo 401k plan. The plan has a separate name and EIN number. We will be able to assist with the EIN if you prefer. You will Provide the name that you would like to assign to your new solo 401k trust. For example, if you are a sole proprietor or a contractor, a common method of naming a solo 401k is to to use a fictitious name followed by Trust. For example, Media Street Trust. Alternatively, if you have a business name, the whole or the first two parts of the business name is commonly used followed by Trust .
Activate Your Solo 401k Formally Elect Your Contributions
While rollovers can happen anytime during the year, the IRS has specific guidelines on when contributions must be made to your plan in order to activate your Solo 4 01k.
There are two types of contributions allowed:
Elective deferrals must be formally elected by December 31st. The actual deposit may be made by the due date of employers return
Formal election simply means you are documenting that you plan to make elective deferrals into your plan, and typically are documenting how much you plan to contribute.
Read Also: Can I Borrow From My 401k For A House
Solo 401k Contribution Deadline 2021
You need to establish your plan and formally elect your contributions before December 31. Do this by filling out the contribution form in the Solo 401k dashboard. You do not have to actually make the contribution until you file your taxes. This depends on what your business structure is. For S Corp, C Corp and Partnership this is March 15, or September 15 if you file an extension. For Sole Proprietorship and Single Member LLC this is April 15 or October 15 if you file an extension. There are many important dates to remember for the Solo 401k. Rather than memorize them, here is a handy article which goes over some of the most important Solo 401k dates to remember.
Contributions And Allocations Are Limited
Contributions to a 401 plan must not exceed certain limits described in the Internal Revenue Code. The limits apply to the total amount of employer contributions, employee elective deferrals and forfeitures credited to the participantâs account during the year. See 401 and Profit-Sharing Plan Contribution Limits.
Read Also: How To Pull Money From Fidelity 401k
Is A Solo 401k The Same As An Individual 401
In the eyes of the law, yes a solo 401k plan is the same as an Individual 401 plan in that they both can only be adopted by a business owner with no employees, or that person and his or her spouse. A solo 401k plan is also commonly called the following:
- One-participant k
However, to retirement account professionals and financial companies a solo 401k is a type of plan that can be self-directed into alternative investments , allows for participant loans, and the mega backdoor strategy. On the other hand, they view the individual 401 as being more restrictive .
My Wife As Trustee Of The Solo 401k Question:
For my business entity/LLC, I am the only member/owner of this LLC. My wife currently is not an owner of this LLC. Can she still be a TRUSTEE in my SOLO-K that we are setting up?
ANSWER
Per our initial conversation, you need to be self-employed with no full-time employees. Moreover, the key in demonstrating that you are self-employed is that you are reporting self-employment activity .
Your wife can be co-trustee in the Solo 401k even if she is not an owner of the LLC and not reporting self-employment activity. Having her as co-trustee will have the benefit of providing you both with signing authority.
You need to report at least some self-employment activity for the year that you open/establish the solo 401k plan on your taxes and going forward. This could be in the form of w-2 wages, activity on Schedule C, etc. Please note that you dont necessarily need to be profitable to receive self-employment income .
Also Check: How To Find 401k From Former Employer
Can I Have A Solo 401k And A Regular 401k
Another frequently asked question that comes up a lot is whether its possible to have a Solo 401k and also have a group 401k plan with your employer. It is possible to have both. Let me tell you how. As long as your employer is offering a 401k plan, you can participate by making employee salary deferrals. This is generally limited to $19,500 or $26,000 if you are age 50 or older.
Now, lets imagine a scenario where you also have a side business or side hustle. You are earning 1099 income driving for Uber on the weekends. You set up a Solo 401k to make additional contributions from your 1099 income to save more for retirement. Keep in mind, the salary deferrals you made at your W2 job follow you. They are aggregated across all 401k plans where you are a participant. So if you maxed out your salary deferral at your job, you cannot put anymore salary deferrals into the Solo 401k.
You can, however, contribute as the employer in the form of a profit sharing contribution which is 20% of your net income from those 1099s. You can also make after-tax contributions, which can be converted into Roth
Turn Your House Into Cash Flow
Are you looking to dip your toe into real estate ? Start by renting out a room in your house on Airbnb. Its a great way to earn some extra cash flow and a short term rental business may qualify as earned income. As we travel more, home-sharing is a more attractive option. The prices are more competitive than a hotel, and you get a local guide to share the experience with. If you own rental properties personally, doing some short-term rentals on Airbnb may be a great way to generate some income and qualify for the Solo 401k plan.
Recommended Reading: How To Use Solar Energy At Home
Also Check: What Is The 401k Limit For 2021
Employee Component: Elective Deferral
Now that weve defined earned income for contribution limit purposes, we can get into the math.
The first component of solo 401 contributions is the elective deferral available to you as your own employee.
For 2020, you can contribute up 100% of your earned income as an employee up to:
- $19,500 for those under 50 years of age as of December 31, 2020, or
- $26,000 for those 50 years of age or older as of December 31, 2020.
It is important to note that if your self-employment income is a side hustle, and if you contribute to your 401 plan through your day job, then you must reduce the employee elective deferral amounts above by any amounts you have contributed to your corporate 401 plan through your employer.
What if you contribute more than is allowed? If you make a mistake and contribute more than the allowable amounts, you can withdraw the excess by April 15, 2021, without penalty, though you will still be subject to tax on any earnings on those overcontributions.
Distribution Rules Must Be Followed
Generally, distributions cannot be made until a “distributable event” occurs. A “distributable event” is an event that allows distribution of a participant’s plan benefit and includes the following situations:
- The employee dies, becomes disabled, or otherwise has a severance from employment.
- The plan ends and no other defined contribution plan is established or continued.
- The employee reaches age 59½ or suffers a financial hardship.
See When can a plan distribute benefits?
Benefit payment must begin when required. Unless the participant chooses otherwise, the payment of benefits to the participant must begin within 60 days after the close of the latest of the following periods:
- The plan year in which the participant reaches the earlier of age 65 or the normal retirement age specified in the plan.
- The plan year which includes the 10th anniversary of the year in which the participant began participating in the plan.
- The plan year in which the participant terminates service with the employer.
Loan secured by benefits. If survivor benefits are required for a spouse under a plan, the spouse must consent to a loan that uses the participant’s account balance as security.
Also Check: Can You Transfer 401k To Td Ameritrade
Contribute To Solo 401k And Day
Your wifes ability to contribute to a solo 401 depends on the self employment income that she receives from the partnership. Specifically, in order to determine how much she could contribute to the solo 401 she would take the amount reported on line 14 of her K-1 and reduce it by one half of the self-employment tax. Of that number, she could contribute for 2021: up to $26,000 as an employee contribution plan sponsored by her daytime employer) and a profit-sharing contribution to the solo 401 equal to 20% of that same number provided that her overall contribution to the solo 401 cannot exceed $64,500 for 2021. For 2022, the overall limit is $67,500.
Solo 401k Rules For Sole Proprietor
Being a sole proprietor is the simplest and easiest way to start out in business. You typically do business under your personal name or you could have a DBA name. Most of the rules for a sole proprietorship are similar to any other business structure, except for a few main areas
When calculating contributions from your sole proprietorship you get to use net business income. Your salary deferral can be up to $19,500 or $26,000 if you are 50 years of age or older. This can be up to 100% of your net business income. Your employer profit sharing contribution is a little bit more complex to calculate. You can look at IRS publication 560 which has a deduction worksheet for self employed in chapter 6. This worksheet helps you calculate your employer profit sharing contribution. Its generally about 20% of your net business income minus half of your self employment income tax. You should work with a qualified tax professional to finalize your numbers. To get an estimate you can also use this Solo 401k calculator.
Your sole proprietorship contributions need to be made before your tax filing deadline. April 15 is the deadline for normal filing. If you file an extension you can make contributions all the way until October 15th. Put your tax deductible contributions on IRS Form 1040, Schedule 1, Line 15. You can write the check to make your contributions from your business checking account and deposit it into your Solo 401k Trust bank or brokerage account.
Read Also: What Is The Penalty For Taking Money Out Of 401k
How To Qualify For A Solo 401k
Michael Atias, director of OTA Tax Pros, explains how investors can generate self-employed income and become qualified for the Solo 401k plan.
Absence of Full-Time Employees
Solo 401k plans, unlike regular 401k plans, can be implemented only by self-employed persons or small-business owners who have no other full-time workers.
An exception exists if the owners spouse is a full-time employee. In that case, the business owner and spouse are technically considered owner-employees rather than employees. In addition to the full-time employee restriction, self-employed owners or operators of a business cannot have any full-time employees working at any other business owned by them or their spouse.
Usually, when a business sets up a retirement plan, it has to include in the plan any full-time employees 21 and older , or part-time employees who work more than 1,000 hours a year. However, companies can employ part-time workers and independent contractors and still be eligible to establish Solo 401k plans.
Solo 401k plan rules exclude from coverage the following types of employees:
- Employees under 21 years of age
- Employees who work less than 1,000 hours per year
- Union employees
Can The Business Exclude Part
In short, yes in the first three years. Starting in 2021 as a result of new solo 401k regulations promulgated under the SECURE Act, part-time employees who work 500 hours but less than 999 hours for three consecutive years will need to be offered the chance to participate in the 401k plan. This new rule did not go into effect until January 2021 therefore, for new solo 401k plans opened in 2021 and those with existing solo 401k plans, the 500 hour count starts in 2021. This means that employees who work 500 hours per year in 2021 through 2023 will become newly eligible in 2024, and they must be allowed to participate. In sum, business owners need to prepare for 2024 by starting in 2021 to track part-time employees hours.
Read Also: Can You Borrow From Your 401k
Minimum Vesting Standard Must Be Met
A 401 plan must satisfy certain requirements regarding when benefits vest. To âvestâ means to acquire ownership. The vested percentage is the participantâs percentage of ownership in his or her account. All participants must be fully vested in their 401 elective deferrals. A traditional 401 plan may require completion of a specific number of years of service for vesting in employer discretionary or matching contributions. For example, a plan may require 2 years of service for a 20% vested interest in employer contributions and additional years of service for increases in the vested percentage. Matching contributions must vest at least as rapidly as a 6-year graded vesting schedule. A safe harbor and SIMPLE 401 plan must provide for 100% vesting in employer and employee contributions at all times.
Read Also: How To Switch From Sole Proprietor To Llc
