See If You Qualify For An Exception To The 10% Tax Penalty
Generally, the IRS will waive it if any of these situations apply to you:
-
You choose to receive substantially equal periodic payments. Basically, you agree to take a series of equal payments from your account. They begin after you stop working, continue for life and generally have to stay the same for at least five years or until you hit 59½ . A lot of rules apply to this option, so be sure to check with a qualified financial advisor first.
-
You leave your job. This works only if it happens in the year you turn 55 or later .
-
You have to divvy up a 401 in a divorce. If the courts qualified domestic relations order in your divorce requires cashing out a 401 to split with your ex, the withdrawal to do that might be penalty-free.
-
You need to pay for COVID-related issues. Section 2022 of the CARES Act says people can take up to $100,000 from their retirement plan, including a 401 penalty free as long as it’s for issues relating to COVID.
Other exceptions might get you out of the 10% penalty if you’re cashing out a 401 or making a 401 early withdrawal:
-
You become or are disabled.
-
You rolled the account over to another retirement plan .
-
Payments were made to your beneficiary or estate after you died.
-
You gave birth to a child or adopted a child during the year .
-
The money paid an IRS levy.
-
You were a victim of a disaster for which the IRS granted relief.
-
You overcontributed or were auto-enrolled in a 401 and want out .
-
You were a military reservist called to active duty.
Taxes If You Withdraw Money In Retirement
When you withdraw money from a 401 in retirement, you will owe taxes in the year when you take the distribution. The withdrawals will be taxed as your other sources of income at your tax bracket rate. At the minimum, you will pay federal income taxes on the distribution. If you are a resident of a state that imposes state income taxes on retirement distributions, you will pay extra taxes. However, certain states don’t tax 401 distributions, and you wonât pay additional taxes.
For Roth 401 withdrawals, you wonât pay income taxes when you withdraw money in retirement, since you had already paid income taxes at the onset. You must have reached 59 ½ and have held the account for five years or more to qualify for tax-free withdrawals from your Roth 401.
If you are already 72, you must start taking the required minimum distributions from a traditional 401 and Roth 401. If you do not take the mandatory distributions, you will incur a 10% penalty on the distribution not taken.
Have Diverse Retirement Income Sources
To be truly efficient with your taxes in retirement, itâs best to have a diverse mix of assets to work with â which means saving for retirement using more than just a 401. This allows you to make strategic withdrawals in retirement that can help you lower your tax burden overall because different assets like Roth accounts, whole life insurance and even annuities have different attributes, including their tax treatment.
You May Like: Is It Better To Contribute To 401k Or Roth 401k
What Are The Rules For A 401 Distribution
You can withdraw money from your 401 penalty-free once you turn 59½. The withdrawals will be subject to ordinary income tax, based on your tax bracket. For those under 59½ seeking to make an early 401 withdrawal, a 10% penalty is normally assessed unless you are facing financial hardship, buying a first home, or needing to cover costs associated with a birth or adoption.
When A Roth 401 Can Make Sense
Taxes are a key consideration when it comes to deciding on a Roth 401 over a traditional 401.
If you’re young and currently in a low tax bracket but you expect to be in a higher tax bracket when you retire, then a Roth 401 could be a better deal than a traditional 401. Think of it this way: With a Roth 401, you can get your tax obligation out of the way when your tax rate is low and then enjoy the tax-free earnings later in life.
The same argument can apply to mid-career workers as well, especially those concerned about the prospects for higher tax rates in the future. After all, current tax rates are fairly low by historical standards. The top rate for married couples filing jointly is 37% in 2022, but it was 70% in 1981 and an eye-watering 91% back in 1963.5
“On the flip side, it may make less sense to contribute to a Roth 401 if you think your tax bracket will be lower in retirement than it is now,” Rob says.
And high earners who expect to maintain their income and spending standards into retirement could consider using Roth 401s to simplify their taxes by paying them up front while they’re still working. Doing this would mean that you would still take RMDs from your Roth 401 but with less of a tax impact since distributions are tax-free. RMDs from a traditional 401, however, would be treated as taxable income.
Recommended Reading: When Can You Start Withdrawing From 401k
Watch Your Tax Bracket
Since all of your 401 distribution is based on your tax bracket at the time of distribution, only take distributions to the upper limit of your tax bracket.
One of the best ways to keep taxes to a minimum is to do detailed tax planning each year to keep your taxable income to a minimum. Say, for example, you are . For 2021, you can stay in the 12% tax bracket by keeping taxable income under $81,050. For 2022, you can stay in the 12% tax bracket by keeping taxable income under $83,550.
Tax Charged On Early Withdrawal
Your 401 retirement savings are meant to help you pay for expenses in your golden years. Taking out a distribution before you are 59 ½ is a bad idea, and it will trigger a 10% penalty on the withdrawal amount. This means you will pay a penalty tax in addition to income taxes.
The tax consequences of an early withdrawal before age 59 ½ include:
- 10% Penalty The IRS will assess a 10% penalty on the distribution. If you withdraw $10,000, the IRS will take a 10% cut from your withdrawal amount i.e. $1000
- 20% withholding tax: The IRS requires employers to withhold 20% of the 401 early withdrawal for payment of income taxes. If you withdraw $10,000 before you are 59 ½, your employer will withhold $2000, and you will receive $8000.
You May Like: How Much Does A 401k Grow Per Year
The Tax Benefits Of Your 401 Plan
OVERVIEW
Your contributions to a 401 may lower your tax bill and help you build financial security.
For information on the third coronavirus relief package, please visit our American Rescue Plan: What Does it Mean for You and a Third Stimulus Check blog post.
Congress created the 401 plan in 1986 to encourage employees of for-profit businesses to save for retirement. Two primary versions exist:
- Tax-deferred 401
- Non-taxed Roth 401 introduced in 2006
Both retirement savings plans offer tax benefits and can help you build financial security for your retirement expenses, such as bills, food, and emergencies.
How Much Tax Will I Pay On A 401 Withdrawal
Because you donât pay taxes on your contributions, your withdrawals will be taxed at your ordinary income rate in retirement. But if you withdraw money from your 401 prior to age 59½, not only will you have to pay taxes, youâll also be hit with a 10 percent penalty. , you wonât pay taxes on your withdrawals in retirement because the money you put in was already taxed â however, you can still be assessed taxes and penalties for taking out your money prior to 59½.)
You May Like: Who Can I Talk To About My 401k
How 401 Deductions Work
Your 401 contributions directly reduce your taxable income at the time you make them, because they’re typically made with pre-tax dollars. You’ll pay taxes on less income as a result.
Exceptions exist for Roth 401 and other after-tax 401 contributions.
Your take-home pay won’t be reduced by the full amount of your contributions. They’re made before withholding is calculated, based on what remains after you’ve made them. These pre-tax contributions reduce your taxable income, and you pay less tax overall.
You’ll often find that what you contribute costs less than you expect, because of the income taxes you save.
Your contributions to a 401 aren’t taxed until you withdrawal them in retirement. Your employer can contribute to your plan as well.
What Is Required 401 Distributions Or Required Minimum Distributions
If you dont take any distributions and reach the age of 70 ½, the IRS will step in and force you to take a distribution. They are called Required Minimum Distributions . The IRSs rationale is hey time to pay up you arent getting any younger. The IRS has a schedule and they will tell you how much your minimum distribution will be. This distribution of course will be considered income and will add to your other income for the affected year.
Assuming your 401 k is traditional and not ROTH, a distribution will be taxed as income. This distribution will be added to your other income for the year and may or may not push you into a higher tax bracket. It would be prudent to seek a tax professional and do some tax planning.
Need Help with understanding Minimum Distributions ?
Read Also: How Can I Pull My 401k Money Out
Roth 401s Reduce Taxes Later
Like tax-deferred 401s, earnings grow tax-free in a Roth 401. However, the Roth 401 earnings aren’t taxable if you keep them in the account until you’re 59 1/2 and you’ve had the account for five years.
Unlike a tax-deferred 401, contributions to a Roth 401 do not reduce your taxable income now when they are subtracted from your paycheck. Contributions to a Roth 401 are after-tax contributions. You are paying taxes as you contribute, so you wont have to pay taxes on the funds or their earnings when you withdraw the money.
- Savers who believe their income and tax rate during retirement will be lower than while working usually opt for a traditional 401.
- Those who predict they will have more income and have a higher tax rate when they retire often prefer the Roth 401.
Among other things, the tax savings you get with a Roth 401 depends partially on the difference between your tax rate while employed and your future tax rate during retirement. When your retirement tax rate is higher than your tax rate throughout your working years, you benefit tax-wise with a Roth 401 plan.
- Taxpayers often have the option of funding both a Roth 401 and a tax-deferred 401.
- The IRS adjusts the maximum contribution amount to account for cost-of-living and announces the annual limits for each type of 401 at least a year in advance.
- Traditionally, the IRS has provided an additional contribution option for savers age 50 and older to enable them to prepare for their pending retirement – $6,500 in 2021.
Rmds: You Do Have To Take Them
There’s a difference between how annual required minimum distributions are handled for a Roth 401 compared to a Roth IRA.
Roth IRAs do not mandate RMDs during the lifetime of the account holder. Roth 401s do. The good news: The money is not taxable, unlike the money you take from a traditional 401. Even better, because Roth 401 distributions are not taxable, they have no impact on the taxability of your Social Security benefits.
The bad news: Once you take a distribution from your Roth 401, that money cannot continue to grow tax-free.
Read Also: How Do I Find A Old 401k
Anything Else I Should Know
Yep. A few things, actually.
Once you contribute to a 401, you should consider that money locked up for retirement. In general, distributions prior to age 59½ will be hit with a 10% penalty and income taxes.
If you leave a job, you can roll your 401 into a new 401 or an IRA at an online brokerage or robo-advisor. The IRA can give you more control over your account and allow you to access a larger investment selection.
401s typically force you to begin taking distributions called required minimum distributions, or RMDs at age 72 or when you retire, whichever is later. You may be able to roll a Roth 401 into a Roth IRA to avoid RMDs.
Penalties And Interest Rates
Q. What are the applicable interest and penalty rates for underpayments of Delaware Income Tax?
A. The interest and penalty rates for underpayment of Delaware Income Tax are as follows:
You May Like: Can I Roll Over A 403b To A 401k
Tax Treatment Of Roth 401 Contributions
A Roth 401 account is a special 401 plan, and it has different tax treatment rules compared to the traditional 401 plan. A Roth 401 plan is funded with after-tax dollars, and the IRS deducts taxes on the contributions you make to the plan. Withdrawal of contributions in retirement is made tax-free, as long as the IRS considers these distributions qualified.
Should You Withdraw Early From Your 401k
Ask yourself honestly . . . are you tempted to cash out your 401k early?
You probably have a long list of all the great things you can do with those funds right now. But is an early withdrawal from your 401k really a good idea?
This 401k Early Withdrawal Calculator will help you compare the consequences of taking a lump-sum distribution from your 401 or even your IRA versus rolling it over to a tax-deferred account.
Make a smart decision. Use the calculator to let the math prove which is the optimum choice.
Read Also: How To Get Money From Your 401k
Avoiding 401 Withdrawal Penalties
To avoid having to make 401 withdrawals, investors should consider taking a loan from their 401. This avoids the 10% penalty and taxes that would be charged on a withdrawal. Another possible option is make sure your withdrawal meets one of the hardship withdrawal requirements.
Note that if you have a Roth 401 you can withdrawal contributions tax-free. Instead of tapping into your 401, you may also be able to use your individual retirement account to avoid the withdrawal penalty. IRAs also charge a 10% penalty on early withdrawals, but they can be avoided if the withdrawal is used for one of the following:
- Unreimbursed medical expenses
- To fulfil an IRS levy
- You’re called to active duty
Borrow Instead Of Withdraw From Your 401
Some plans let you take out a loan from your 401 balance. If so, you may be able to borrow from your account, invest the funds, and create a consistent income stream that persists beyond your repayment of the loan.
The IRS generally allows you to borrow up to 50% of your vested loan balanceup to $50,000with a payback period of up to five years. In this case, you don’t pay any taxes on this distribution, let alone a 10% penalty. Instead, you simply have to pay back this amount in at least quarterly payments over the life of the loan.
With these parameters, consider this scenario: You take out a $50,000 loan over five years. With interest, let’s say your monthly payment over this 60-month period is $900. Now imagine taking that $50,000 principal amount and purchasing a small house, apartment, or duplex in the relatively inexpensive South to rent out. Given that you would be purchasing this property without a mortgage let’s say that your net rent each month comes out to $1,100, after taxes and management fees.
What you have effectively done is set up an investment vehicle that puts $200 in your pocket each month for five years. And after five years, you will have fully paid back your $50,000 401 loan, but you’ll continue to pocket your $1,100 net rent for life! You might also have the opportunity to sell that house/apartment/duplex later on at an appreciated amount, in excess of inflation.
Read Also: Can I Transfer Rollover Ira To 401k
Do You Pay Tax On 401 Contributions
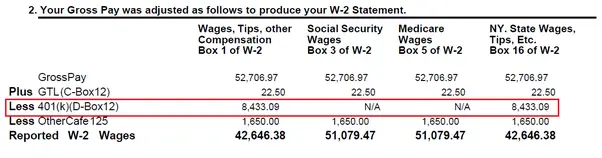
A 401 is a tax-deferred account. That means you do not pay income taxes when you contribute money. Instead, your employer withholds your contribution from your paycheck before the money can be subjected to income tax. As you choose investments within your 401 and as those investments grow, you also do not need to pay income taxes on the growth. Instead, you defer paying those taxes until you withdraw the money.
Keep in mind that while you do not have to pay income taxes on money you contribute to a 401, you still pay FICA taxes, which go toward Social Security and Medicare. That means that the FICA taxes are still calculated based on the full paycheck amount, including your 401 contribution.
