Impact Of A 401 Loan Vs Hardship Withdrawal
A 401participant with a $38,000 account balance who borrows $15,000 will have $23,000 left in their account. If that same participant takes a hardship withdrawal for $15,000 instead, they would have to take out $23,810 to cover taxes and penalties, leaving only $14,190 in their account, according to a scenario developed by 401 plan sponsor Fidelity. Also, due to the time value of money and the loss of compounding opportunities, taking out $23,810 now could result in tens of thousands less at retirement, maybe even hundreds of thousands, depending on how long you could let the money compound.
Better Options For Emergency Cash Than An Early 401 Withdrawal
We know it can be a struggle when suddenly you need emergency cash for medical expenses, student loans, or crushing consumer debt. The extreme impact of coronavirus on public health and the economy has only compounded some of the more routine challenges of consumer cash flow.
We get it. The money squeeze can be quick and traumatic, especially in a more volatile economy.
Thats why information about an early 401 withdrawal is among the most frequently searched items on principal.com. Understandably so, in a world keen on saddling us with debt.
But the sad reality is that if you do it, you could be missing out on crucial long-term growth, says Stanley Poorman, an advice and planning manager for Principal® Advised Services who helps clients on household money matters.
In short, he says, Youre harming your ability to reach retirement. More on that in a minute. First, lets cover your alternatives.
Loans To Purchase A Home
Regulations require 401 plan loans to be repaid on an amortizing basis over not more than five years unless the loan is used to purchase a primary residence. Longer payback periods are allowed for these particular loans. The IRS doesn’t specify how long, though, so it’s something to work out with your plan administrator. And ask whether you get an extra year because of the CARES bill.
Also, remember that CARES extended the amount participants can borrow from their plans to $100,000. Previously, the maximum amount that participants may borrow from their plan is 50% of the vested account balance or $50,000, whichever is less. If the vested account balance is less than $10,000, you can still borrow up to $10,000.
Borrowing from a 401 to completely finance a residential purchase may not be as attractive as taking out a mortgage loan. Plan loans do not offer tax deductions for interest payments, as do most types of mortgages. And, while withdrawing and repaying within five years is fine in the usual scheme of 401 things, the impact on your retirement progress for a loan that has to be paid back over many years can be significant.
If you do need a sizable sum to purchase a house and want to use 401 funds, you might consider a hardship withdrawal instead of, or in addition to, the loan. But you will owe income tax on the withdrawal and, if the amount is more than $10,000, a 10% penalty as well.
You May Like: Should You Always Rollover Your 401k
Tests For A 401 Hardship Withdrawal
The six tests for a hardship withdrawal did not change with the new law. Hardship withdrawals are permissible due to a heavy financial due to the following:
For 2020, there is an additional reason under the CARES Act: being negatively affected by COVID-19.
From 2018 to 2025, the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act declared such losses are not tax-deductible except in specified federal disaster areas. It should be noted that the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act also reduced the threshold for individuals deducting for medical expenses to those that exceed 7.5% of adjusted gross income for 2017 and 2018. However, that threshold rose back to 10% of AGI, starting in the 2019 tax year.
You Will Be Taxed On 401 Distributions
Traditional 401 contributions are often made on a pretax basis, which means they lower your taxable income during your working years.
Because the money wasnât taxed when you contributed it, when you begin taking distributions from your 401, youâll have to pay tax because the IRS treats this money as ordinary income. That means you wonât get to keep everything youâve saved. And if you withdraw too much in a given year, you could push yourself into a higher tax bracket â meaning the government will take a larger portion of your savings.
While you will owe income tax on money that you withdraw from a traditional 401, you will not owe tax on money that you have saved in a Roth 401. If your savings is in a traditional account, itâs possible to do a Roth conversion, where you will owe income tax on the amount you convert in the year that you convert it. With a Roth IRA, you can enjoy tax-free distributions in retirement.
So how does a 401 work in retirement? While it can be rolled to an IRA, ultimately itâs up to you and how you want to use your lifetime of savings to generate the income you need to fund the things youâve been dreaming about for your retirement. An experienced financial advisor who understands the ins and outs of retirement income and tax planning can help.
Recommended Reading
You May Like: How Do You Roll A 401k Into An Ira
Finding A Good Withdrawal Rate
One widely used rule of thumb on withdrawal rates for tax-deferred retirement accounts states that withdrawing slightly more than 4% annually from a balanced portfolio of large-cap equities and bonds would provide inflation-adjusted income for at least 30 years.
However, some experts contend that a higher withdrawal rate may be possible in the early, active retirement years if later withdrawals grow more slowly than inflation. Others contend that portfolios can last longer by adding asset classes and freezing the withdrawal amount during years of poor performance. By doing so, they argue, “safe” initial withdrawal rates above 5% might be possible.
Don’t forget that these hypotheses were based on historical data about various types of investments, and past results don’t guarantee future performance. There is no standard rule of thumb that works for everyoneâ your particular withdrawal rate needs to take into account many factors, including, but not limited to, your asset allocation and projected rate of return, annual income targets , and investment horizon.
What Are Qualified Distributions
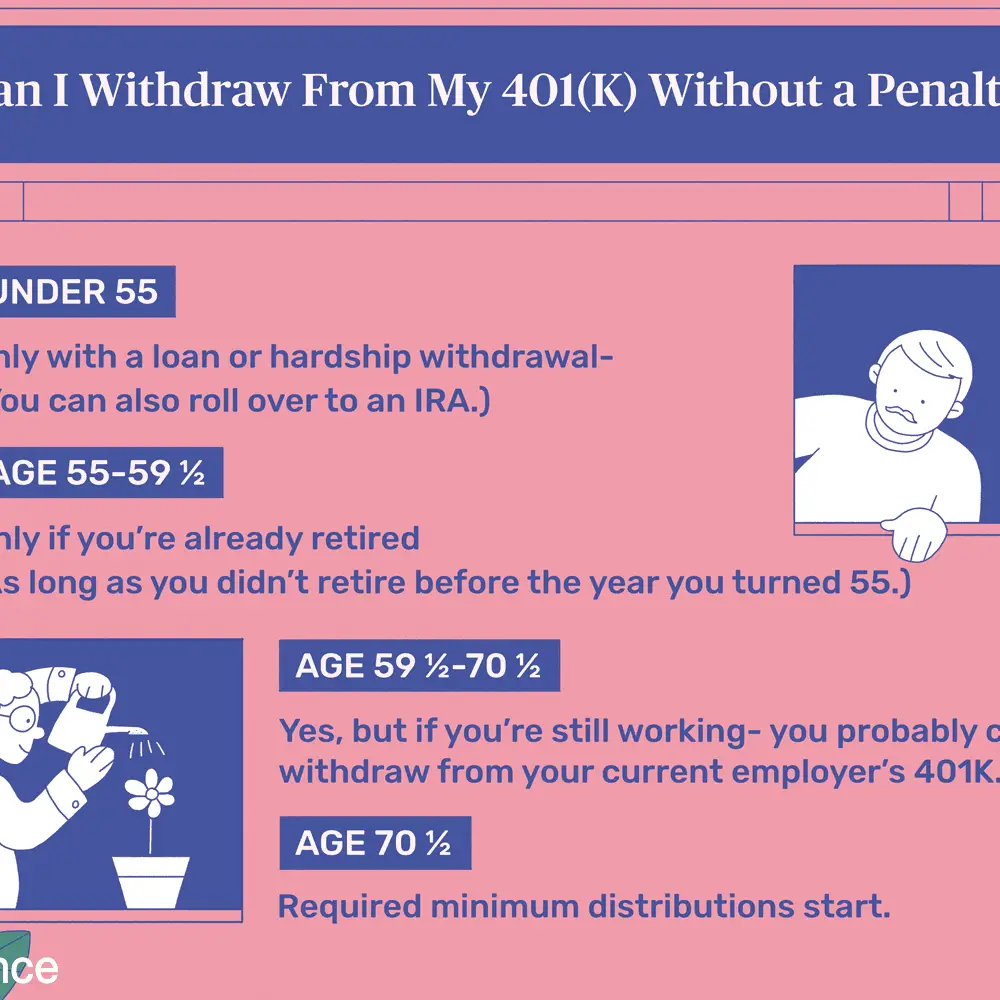
Qualified distributions are those that can be taken made tax-free and penalty-free. They’re taken after age 59 1/2 or under some other allowed circumstances.
There’s no penalty for withdrawing your money after you reach age 59 1/2, but you’ll pay income tax on the money you take out if you’ve invested in a traditional pre-tax 401 or a traditional IRA with untaxed dollars. You took a tax deduction at the time you made the contributions.
Roth IRAs and Roth 401 contributions are made with after-tax dollars. These distributions aren’t taxed when you take withdrawals, but you must have owned the Roth account for five years or longer.
It’s best to begin taking money from tax-deferred accountsthose for which you claimed tax deductionsafter you retire. You might be in a lower tax bracket at that time, because you’ll no longer be earning income from working.
You May Like: Why Rollover Old 401k To Ira
Taking Money Out Of A 401 Once You Leave Your Job
If you no longer work for the company that sponsored your 401 plan, first contact your 401 plan administrator or call the number on your 401 plan statement. Ask them how to take money out of the plan.
Since you no longer work there, you cannot borrow your money in the form of a 401 loan or take a hardship withdrawal. You must either take a distribution or roll your 401 over to an IRA.
Any money you take out of your 401 plan will fall into one of the following three categories, each with different tax rules.
A 401 Is One Source Of Retirement Income
Remember that a 401 on its own is not a retirement income plan. While itâs certainly a smart way to save for your future and plays an integral part in building your nest egg, a 401 is just one source of income in retirement.
A plan to create income in retirement will certainly take your 401 into consideration. But it should also include income withdrawals from other accounts like IRAs, Roth IRAs, investments, cash value built up within a whole life insurance policy and cash reserves. Your retirement plan will also include income from Social Security, and may include income from annuities and pensions. By having multiple streams of income, you can more efficiently generate retirement income by strategically leaning on different sources at different times. This approach can help you minimize taxes while balancing the need to grow your investments and generate reliable income that will last through your retirement.
Recommended Reading: Can You Withdraw Your 401k If You Quit Your Job
You Must Begin Taking Distributions At Age 72
Even if you donât need the money, youâll have to start taking required minimum distributions from your 401 beginning at age 72. The same goes for any other tax-deferred retirement accounts you may have. , you can get around this by converting these funds to a Roth IRA. However, you wonât owe any taxes on the money in a Roth 401, and itâs distributed proportionately.)
The amount youâre required to withdraw depends on your retirement account balances and your life expectancy. While these IRS worksheets can help you do the math, a financial advisor can help you think about how to be effective with your distributions.
Understanding Early Withdrawal From A 401
The method and process of withdrawing money from your 401 will depend on your employer and the type of withdrawal you choose. Withdrawing money early from your 401 can carry serious financial penalties, so the decision should not be made lightly. It’s really a last resort.
Not every employer allows early 401 withdrawals, so the first thing you need to do is check with your human resources department to see if the option is available. If it is, then you should check the fine print of your plan to determine the type of withdrawals that are allowed or available.
As of 2021, if you are under the age of 59½, a withdrawal from a 401 is subject to a 10% early withdrawal penalty. You will also be required to pay normal income taxes on the withdrawn funds. For a $10,000 withdrawal, once all taxes and penalties are paid, you will only receive approximately $6,300. There are some non-penalty options to consider, however.
Before deciding upon taking an early withdrawal from your 401, find out if your plan allows you to take a loan against it, as this allows you to eventually replace the funds. You may also want to consider alternative options for securing financing that could hurt you less in the long run, such as a small personal loan.
Recommended Reading: What Is Ira And 401k
When You Leave A Job
When you leave a job, you generally have the option to:
- Leave your 401 with your current employer
- Roll over the funds to an IRA
- Roll over the funds to your new employer’s 401.
If you choose any of those options, you will not owe taxes or a 10% penalty. You can also take this money as a distribution, but this will trigger early-withdrawal penalties if you are under 59 1/2 .
When A Problem Occurs
The vast majority of 401 plans operate fairly, efficiently and in a manner that satisfies everyone involved. But problems can arise. The Department of Labor lists signs that might alert you to potential problems with your plan including:
- consistently late or irregular account statements
- late or irregular investment of your contributions
- inaccurate account balance
Also Check: How Much To Invest In 401k To Be A Millionaire
Understanding The Rules For 401 Withdrawal After 59 1/2
-
Waives the 10% early withdrawal penalty
-
Allows retirees to forgo taking Required Minimum Distributions from a 401 in 2020.
A 401 is a type of investment account thats sponsored by employers. It lets employees contribute a portion of their salary before the IRS withholds funds for taxes, which allows interest to accumulate faster to increase the employees retirement funds. Now, if you have a 401, you could pay a penalty if you cash out your investment account before you turn 59 ½. Heres some more information about the rules you need to follow to maximize your 401 benefits after you turn 59 ½.
Retirement Savings Can Benefit
As you make loan repayments to your 401 account, they usually are allocated back into your portfolio’s investments. You will repay the account a bit more than you borrowed from it, and the difference is called “interest.” The loan produces no impact on your retirement if any lost investment earnings match the “interest” paid ini.e., earnings opportunities are offset dollar-for-dollar by interest payments.
If the interest paid exceeds any lost investment earnings, taking a 401 loan can actually increase your retirement savings progress. Keep in mind, however, that this will proportionally reduce your personal savings.
Read Also: Should I Do Roth Or Traditional 401k
K Withdrawal Rules: How To Avoid Penalties
401k plans, IRAs and other tax-advantaged retirement savings accounts are common ways to save for retirement, and millions of Americans pour money into them every year. Its generally wise to avoid withdrawing money from your 401k, as there are often hefty penalties and taxes to consider for early withdrawals.
Sometimes, however, unplanned circumstances force people to withdraw funds from their 401k early. So if you find yourself in a place where you need to tap your retirement funds early, here are some rules to be aware of and some options to consider.
Helpful In Other Years: Bipartisan Budget Act Changes
There is other good news about accessibility: The Bipartisan Budget Act passed in January 2018 issued new rules that will make it easier to withdraw a larger amount as a hardship withdrawal from a 401 or 403 plan:
An additional change for 2019 was that you are no longer required to take a plan loan before you become eligible for a hardship distribution. However, whether or not you will be allowed to take a hardship distribution is a decision that still remains with your employer. Your employer may also limit the uses of such distributions, such as for medical or funeral costs, as well as require documentation.
Although a hardship withdrawal might be eligible to avoid the 10% penalty, it still incurs income taxes on the sum you withdraw.
Recommended Reading: Do Employers Match Roth 401k
When Faced With A Sudden Cash Crunch It Can Be Tempting To Tap Your 401 More Than A Few Individuals Have Raided Their Retirement Account For Everything From Medical Emergencies To A Week
But if you’re under 59-1/2, keep in mind that an early withdrawal from your 401 will cost you dearly. You’re robbing your future piggy bank to solve problems in the present.
You’ll miss the compounded earnings you’d otherwise receive, you’ll likely get stuck with early withdrawal penalties, and you’ll certainly have to pay income tax on the amount withdrawn to Uncle Sam.
If you absolutely must draw from your 401 before 59-1/2, and emergencies do crop up, there are a few ways it can be done.
Hardship withdrawals
You are allowed to make withdrawals, for example, for certain qualified hardships — though you’ll probably still face a 10% early withdrawal penalty if you’re under 59-1/2, plus owe ordinary income taxes. Comb the fine print in your 401 plan prospectus. It will spell out what qualifies as a hardship.
Although every plan varies, that may include withdrawals after the onset of sudden disability, money for the purchase of a first home, money for burial or funeral costs, money for repair of damages to your principal residence, money for payment of higher education expenses, money for payments necessary to prevent eviction or foreclosure, and money for certain medical expenses that aren’t reimbursed by your insurer.
Loans
Most major companies also offer a loan provision on their 401 plans that allow you to borrow against your account and repay yourself with interest.
You then repay the loan with interest, through deductions taken directly from your paychecks.
Taxes For Making An Early Withdrawal From A 401
The minimum age when you can withdraw money from a 401 is 59.5. Withdrawing money before that age results in a penalty worth 10% of the amount you withdraw. This is in addition to the federal and state income taxes you pay on this withdrawal.
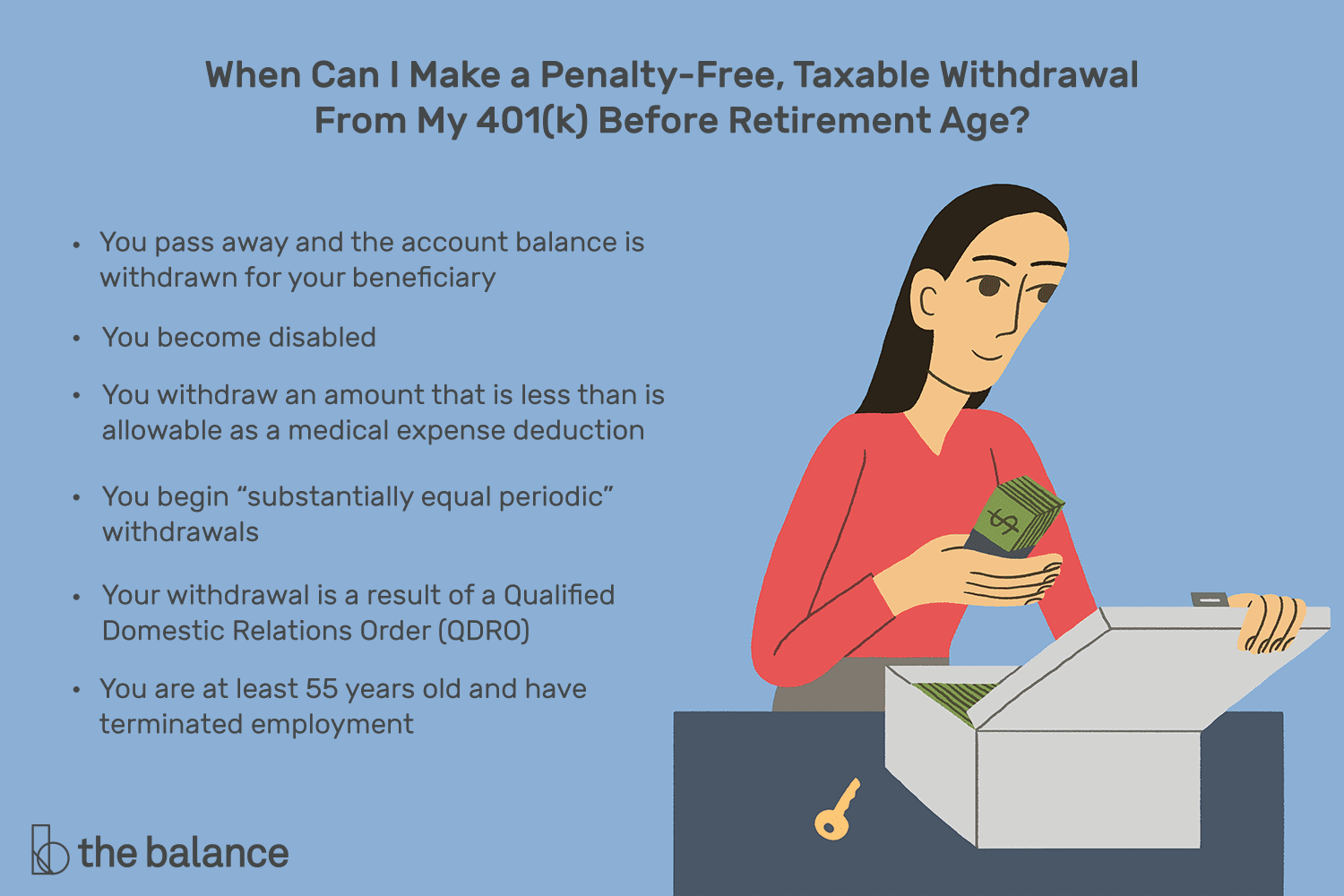
There are exceptions to this early withdrawal penalty, though.
If you want to remove money from a 401 account without paying taxes, you will need to meet certain criteria. According to the IRS, you generally dont have to pay income tax or an early withdrawal penalty if you experience an immediate and heavy financial need. One situation where this may apply is when you have medical expenses that arent reimbursed by your insurance and which exceed 7.5% of your adjusted gross income . If this happens, you dont have to pay taxes on the money you withdraw to cover that financial need. There are also other exceptions, such as for disabled taxpayers. The IRS provides a more complete list of situations where you wont pay tax on early withdrawals.
The big caveat here is that the amount you can withdraw tax-free is exactly enough to cover the cost of this financial need. And youll still pay the full income tax on your withdrawal only the 10% penalty is waived.
Read Also: Where Can I Get 401k Plan
