Do You Qualify For A Self
Are you a self-employed professional planning for your retirement? A self-employed 401 is an excellent plan to build out your retirement nest egg. Whether you are a freelancer, shop owner, or small business owner without employees, a solo 401 retirement plan can help you live your dream life when you retire. Here well discuss an overview of a self-employed 401, setting one up, how to withdraw from the account and other vital information.
How A Solo 401 Works
Solo 401s are available only to self-employed workers with no employees, with an exception for business owners who employ their spouses. To open one of these accounts, you must have an employer identification number , which you can get from the U.S. Internal Revenue Service .
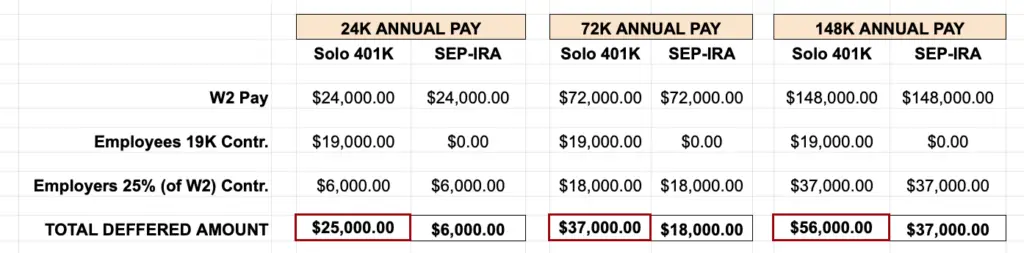
You’re allowed to make two types of contribution to your solo 401: an employee contribution and an employer contribution. Your employee contribution limit is the same as the 401 contribution limit for any traditionally employed worker — $19,500 in 2021, or $26,000 if you’re 50 or older.
If you’d like to contribute more than this, you can make additional contributions as an employer, but this calculation is a little more complicated. You may contribute up to 25% of your net self-employment income for the year. That is all the money you’ve earned from your business minus any business expenses, half of your self-employment taxes, and the money you contributed to your solo 401 as an employee contribution.
Only the first $290,000 in net self-employment income counts for the year, and the total amount you may contribute to your solo 401 as employee and employer in 2021 is $58,000, or $64,500 if you’re 50 or older.
If you find yourself in need of cash later on, you can take a loan from your solo 401 just as you can from a traditional 401. Typically, you’re limited to the lesser of 50% of your balance or $50,000, but the government has doubled these limits in 2020 to help those affected by the pandemic.
Who Is Eligible For A Solo 401
Solo 401 plans are intended for the self-employed. If you have employees and are looking for a retirement plan, then you have other options such as the or SIMPLE IRA, both of which allow you to provide tax-advantaged benefits to your employees. A lesser-known program called a SIMPLE 401 also allows businesses to set up retirement plans.
While solo 401 plans are intended for one-person businesses, there is an exception. The spouse of the business owner can also participate in the plan. With a spouse in the plan, your small business can really stash away cash for retirement. A qualifying couple could save as much as $114,000 annually in the plan, and even more if they were eligible for catch-up contributions.
Read Also: Do I Have To Pay Taxes On 401k Rollover
Should You Contribute To A Roth Solo 401
Tax decisions are very individualized. You should consult your tax advisor before taking action. But to help give you a working knowledge of this area, the following are some of the factors that indicate you should strongly consider contributing to a Roth Solo 401 instead of to a Traditional Solo 401:
- Youth
- Low/modest income
- Long investment time horizon
- Increased likelihood that your current combined federal and state marginal income tax rate is lower than your future combined marginal income tax rate
- Desire to insure against increases in future income tax rates
How Do You Set Up A Self
It is easy to set up a self-employed 401 plan with many 401 administrators. You can also open a solo 401 online. To set one up, you will need an Employer Identification Number , which you can get from the IRS. You also need to complete a plan adoption agreement and an account application. Self-employed 401s are easy to administer and attract low maintenance fees because they involve only one or two people.
Before choosing a plan administrator, it is important to compare their fees before you sign up. You may also want to choose an administrator that allows you to invest your retirement savings into a broad range of assets including mutual funds, ETFs, CDs, stocks, and bonds. Other features to look for include 24-hour multi-channel support, investment advisory, low fees, and positive customer reviews. Once youve completed the paperwork, and the plan becomes active, the only thing you have to do is to set contribution levels and choose investments.
Self-employed 401 plans have no annual minimum contribution requirements. In good years, you can make the maximum contributions and reduce your savings when the cash flow is low. But once you have up to $250,000 in the account, you must file IRS Form 5500-EZ to report the financial status of your solo retirement plan to the tax authorities.
Don’t Miss: How Much Should I Put In My 401k
Contributions To A Traditional 401 Reduce Your Taxable Income
Eric is currently a duly licensed Independent Insurance Broker licensed in Life, Health, Property, and Casualty insurance. He has worked more than 13 years in both public and private accounting jobs and more than four years licensed as an insurance producer. His background in tax accounting has served as a solid base supporting his current book of business.
Contributions to qualified retirement plans such as traditional 401 plans are made on a pre-tax basis, which removes them from your taxable income and thus reduces the taxes you’ll pay for the year.
There are limits to how much you can contribute tax-free to such a plan. For 2020 and 2021, the annual limit is $19,500. Those who are 50 or older can almost alwaysit’s allowed by 98% of plans make an additional catch-up contribution each year of $6,500. You can even contribute the catch-up when you are 49, provided you will turn 50 before the end of the calendar year.
Sole Proprietorship Or Single Member Llc
Imagine that Stephanie, 35 years old, is a sole proprietor and has $125,000 in self employment income on Schedule C of her tax return. Stephanie may make $19,500 in employee deferrals. She may also make a profit sharing contribution of 25% of her adjusted earned income: $92,935. Adjusted earned income is calculated as: / .
/ = $92,935. 25% of this amount works out to $23,233. Stephanies total contribution between elective deferrals and profit sharing contributions would be $42,733.
Recommended Reading: How To Start My Own 401k
Qualifying For A Solo Roth 401
One-participant 401, Solo 401, and Solo Roth 401 plans are tax-advantaged retirement accounts for the self-employed or for business owners with no full-time employees. These plans may also be called Self-Directed 401, Individual 401, Individual Roth 401, Self-Employed 401, Personal 401 or One-Participant 401, Solo 401, Solo-k, Uni-k, or One-Participant k depending on the vendor offering the plan. Qualifying for a Solo 401 requires earned income, which is also true for a 401, SEP plan, IRA etc. As with the traditional IRA and Roth IRA, the difference between a Solo 401 and Solo Roth 401 is that the Solo 401 involves tax-deductible savings and taxable withdrawals. The Solo Roth 401 involves already-taxed savings and tax-free withdrawals. Most other features of these two Solo plans are the same, including tax-free growth. I will use the terms interchangeably except when discussing their tax implications.
Recall that the Solo 401 plan is for businesses with no full-time employees. There is one exceptiona spouse who earns income from the business. Your spouse, as a full-time employee, can make the same employee contribution you can make as the business owner up to the legal limits, including catch-up provisions, if he or she has qualifying income. In addition, you as the owner can provide the same percentage of employer contribution to your spouse that you give yourself, up to 25% of compensation.
Next Steps To Consider
Keep in mind that investing involves risk. The value of your investment will fluctuate over time, and you may gain or lose money.
The change in the RMD age requirement from 70½ to 72 only applies to individuals who turn 70½ on or after January 1, 2020. Please speak with your tax advisor regarding the impact of this change on future RMDs.
Fidelity does not provide legal or tax advice. The information herein is general and educational in nature and should not be considered legal or tax advice. Tax laws and regulations are complex and subject to change, which can materially impact investment results. Fidelity cannot guarantee that the information herein is accurate, complete, or timely. Fidelity makes no warranties with regard to such information or results obtained by its use, and disclaims any liability arising out of your use of, or any tax position taken in reliance on, such information. Consult an attorney or tax professional regarding your specific situation.
This information is intended to be educational and is not tailored to the investment needs of any specific investor.
Read Also: Can I Roll My Roth 401k Into A Roth Ira
How To Open A Solo 401
- Apply for an EIN with the IRS: Before you can open a solo 401, you need to obtain an employer identification number . You can apply for one of these on the IRS website if your principal business is based in the United States or its territories. You’ll need a valid taxpayer ID, such as a Social Security number, to apply for an EIN. As soon as you’ve completed the application and the IRS has verified your information, it will send you an EIN.
- Find a brokerage: Next you must decide where you’re going to open your solo 401. You can do so with just about any broker. The choice comes down to fees, investment options, and customer service. Explore a few different options before deciding which one is the best fit for you right now. It’s not set in stone — you can always do a rollover later — but rather than going through all that hassle, take the time to choose your broker carefully.
- Meet the annual deadlines: You must have opened your solo 401 by Dec. 31, 2020, to make contributions for the 2020 tax year. You must also have made your employee contribution by the end of the year, although you have until the revised tax deadline — May 17, 2021 — to make your employer contribution for the year. If you decide to make a 2020 solo 401 contribution in 2021, make sure your broker applies your contribution correctly. Some may default to a current-year contribution, and that can cause problems between you and the IRS if you try to write off those contributions on your 2020 taxes.
Contribution Limit As An Employer
Wearing the employer hat, you can contribute up to 25% of your compensation. The total contribution limit for a solo 401 is $57,000 for 2020, not counting the employee’s $6,500 catch-up amount for those over the age of 50. For 2021, the employer maximum is $58,000. In other words, in 2021 you can contribute $58,000 along with a $6,500 catch-up contribution if applicable for a total of $64,500 for the year.
You May Like: Do Employers Match Roth 401k
What Are Tax Savers Credits
Making eligible contributions to an employer-sponsored retirement plan such as a 401 or an IRA can potentially lead to a tax credit known as a Retirement Savings Contributions Credit, or a Savers Credit . There are certain eligible requirements that must be met to qualify for this credit.
1. Individual must be age 18 or older2. They can not be claimed as a dependent on someone elses return3. They can not be a student The amount of the credit received depends on the individuals adjusted gross income reported on their Form 1040 series return. The credit amount is typically 50%, 20% or 10% of:
Elective salary deferral contributions made to a 401, 403, governmental 457, SARSEP, or SIMPLE plan Contributions made to a traditional or Roth IRA Voluntary after-tax employee contributions made to a qualified retirement plan or 403 plan, contributions to a 501 plan, or contributions made to an ABLE account for which you are the designated beneficiary
For 2020 the maximum contribution amount that qualifies for this credit is $2,000 for individuals and $4,000 for married couples filing jointly, bringing the maximum credit to $1,000 for individuals and $2,000 for those filing jointly. Rollover contributions dont qualify for this credit.
Solo Roth 401 Gives Self
Doctor video chatting about solo Roth 401 by video chat.
Getty
Many self-employed business owners lament the fact that they do not have a corporate company 401 plan. They must not be aware that they can set up their own 401 plan that has even more flexibility than a corporate one. And those who do know this usually investigate the plan only for the tax advantages, but they should also be thinking of the retirement benefits.
Recently, I was talking to a doctor who is planning to go into business for himself. He elected to incorporate as an S Corp. He had accounts from prior employers and was wondering what to do with them. In his business he will not have any employees. I suggested he investigate a Roth Solo 401, which really should be called a Solo Roth 401, profit sharing plan.
Recommended Reading: How To Find My 401k Money
Can You Contribute A Lump Sum To A Self
According to Bergman, a self-employed individual can usually make an employee deferral lump-sum contribution to a plan so long as he or she has sufficient earned income. However, in the case of a W-2 owner/employee, the employee deferral contribution should not be more than the income earned for that income period. In the case of employer profit-sharing contributions, those can be made by the employer in a lump sum.
Roth Ira Income Limits
Unlike a Traditional IRA where deductions are impacted by participation in an employer retirement plan, a Roth IRA is simply limited by your AGI.
Single filers can make a full Roth IRA contribution if their AGI is below $129,000. Partial contributions are allowed up to $144,000. The prior phase out range in 2021 was between $124,000 and $140,000.
For married filers, the new Roth phase out range is from $204,000 to $214,000. This is a nice increase from the 2021 limits set between $198,000 and $208,000.
Read Also: How Much You Should Contribute To 401k
What Are The Factors That Differentiate The Solo 401 From An Employer 401
Three main factors distinguish a self-employed 401 plan from an employer 401 including:
-
You are the employer and employee on the plan as the business owner.
-
Solo 401 plans allow you to make far higher contributions to your retirement plan than if you are an employee in an employer 401.
-
Any self-employed person can open a solo 401 plan regardless of the product or service you provide.
You can also run a self-employed 401 account as a self-directed plan. It allows you to invest your contributions on specific assets with an investment broker trustee.
A solo 401 plan is ideal if you want to set up a retirement plan as a self-employed person. It has the highest contribution restrictions, which allows you to grow your retirement savings faster and you can also enjoy solo 401 tax benefits. It is also easy to set up and administer.
Self-employed 401 plans give you complete control of your investment choices if you open them in a self-directed brokerage account. If your business hires employees at a later date, you only need to convert the solo 401 account into a standard employer 401 plan.
Article By
The Human Interest Team
We believe that everyone deserves access to a secure financial future, which is why we make it easy to provide a 401 to your employees. Human Interest offers a low-cost 401 with automated administration, built-in investment advising, and integration with leading payroll providers.
Solo 401 Contribution Limits For 2019
The maximum amount a self-employed individual can contribute to a solo 401 for 2019 is $56,000 if he or she is younger than age 50. Individuals 50 and older can add an extra $6,000 per year in “catch-up” contributions, bringing the total to $62,000. Whether you’re permitted to contribute the maximum, though, will be determined by your self-employment income.
You are allowed to sock away so much because you can make contributions as both an employee and an employer, though each type of contribution to a solo 401 has its own IRS rules.
For instance, you can contribute up to $19,000 for 2019 as an employee , even if that is 100% of your self-employed earnings for the year. Contributions are made on a pre-tax basis, although some solo 401 providers also offer a Roth 401 option that allows you to invest some or all of your contributions on an after-tax basis. Pre-tax contributions and their earnings will be taxed as regular income when withdrawn in retirement Roth contributions will be tax-free in retirement.
In addition, you effectively can contribute up to 20% of your net self-employment income as an employer , though those contributions must be made with pre-tax dollars. These pre-tax contributions lower your taxable income and help cut your tax bill.
Employee contributions generally must be made by the end of the calendar year, but you have until the tax-filing deadline to make employer contributions.
Recommended Reading: How Can I Get Money Out Of My 401k
What Is A Self
This plan goes by many names, including solo, individual and single-k, but they all refer to a 401 retirement savings plan for a self-employed person. You can contribute a large amount of money to this plan every year and then start taking distributions from the account after you turn 59.5 years of age.
Key takeaway: A self-employed 401 plan is a retirement savings plan started and contributed to by a self-employed person.
