Traditional Vs Roth 401/403 Analyzer
Which option is best for you?
If your 401 or 403 retirement plan accepts both traditional and Roth contributions, you have two ways to save for your retirement. Both offer federal income tax advantages.
Traditional accounts provide a tax break now. Traditional 401/403 contributions are not taxed at the time of investment. Instead, taxes are paid on withdrawals, including any earnings. Getting a tax break at the time of investment will leave more money in your pocket now money that you can invest, save or spend.
Roth accounts provide a tax advantage later. Roth 401/403 contributions are made with money thats already been taxed, so you wont have to pay taxes on qualified withdrawals, including earnings.
Enter your personal information to compare the results of traditional before-tax savings and Roth after-tax savings. Click on each question for help and additional information.
Investments are not FDIC-insured, nor are they deposits of or guaranteed by a bank or any other entity, so they may lose value. Investors should carefully consider investment objectives, risks, charges and expenses. This and other important information is contained in the fund prospectuses and summary prospectuses, which can be obtained from a financial professional or and should be read carefully before investing.
Copyright 2021 American Funds Distributors, Inc.
Vs : What’s The Difference And Which Is Better For You
TheStreet
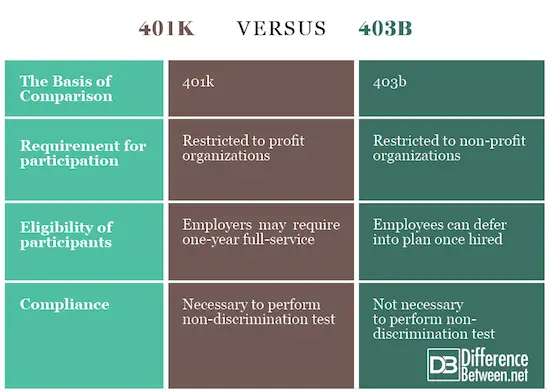
401 plans and 403 plans have much in common – and several key distinctions. It pays to know about both retirement plans.
401’s and 403’s are the most widely used employer-sponsored retirement plans in the U.S.
Each plan allows participants to steer money from their paychecks to invest for retirement, earning tax-deferred interest along the way. With both 401’s and 403’s, taxes are taken out of withdrawals after reaching retirement, and not contributions made while on the job.
Both 401 and 403 plans are highly useful for Americans trying to sock away some cash for retirement, yet both have important differences and distinctions that set them apart from one another, and that offer ample retirement savings benefits to qualified users.
Here’s a snapshot of each plan:
How Can I Contribute To A 401k Or 403b
The difference in overall cost between a 401 and a 403 can be either small or substantial. Plan costs are most directly determined by:
By law, 403 organizations are exempt from certain administrative processes that apply to 401 plans. This allows organizations with very small budgets to help their employees save for retirement. For this reason, administrative costs are generally lower for 403 plans than 401 plans.
There are three types of contributions that can be made to your 401k or 403b account:
Recommended Reading: How To Transfer My 401k To My Bank Account
Required Minimum Distribution Options For 401 And 403 Plans
Largely, minimum distributions are the same for both 401 plans and 403 plans – but there are some variances.
For example, both 401 and 403 plans require plan participants to begin taking minimum distributions out at age 70 and a half. The required distributions must begin once the account holder is age 70 ½, regardless of whether the plan participant is retired.
For 403 plans, since the cash taken out is after-tax money, required minimum distributions will not boost your taxable income. Additionally, any missed required minimum distributions for both 401 and 403 plans will trigger a 50% tax penalty of the distribution amount.
Do I Have To Contribute To A 401 Or 403
Same. No, not at all. Both plans are voluntary. But unless youve got gold bricks hiding somewhere, youd be foolish not to.
Again: Remember that whatever you save for retirement is likely all youll ever have. Taking advantage of tax-deferred retirement savings plans like this give you a big break by not charging you taxes on your savings. In addition, the earlier you start, the more they help you take advantage of the power of compounding returns over time.
Read Also: How Do You Max Out Your 401k
Vs : Whats The Difference
6 Minute Read | September 27, 2021
What pops into your head when you hear 403 or 401? No, these arent droids from the latest Star Wars movie. Theyre tools to help you build a solid financial future! And if youre going to invest your hard-earned money in one of these plans, you need to fully understand how they work.
Last year, our team conducted the largest research study ever done on millionaires. Do you know what their number one wealth-building tool is? Their 401 or 403. Nearly eight out of 10 millionaires built their wealth primarily through their workplace retirement plan. So, if youre wondering about the differences between a 403 and a 401, youre in good company! Youre thinking like a millionaire.
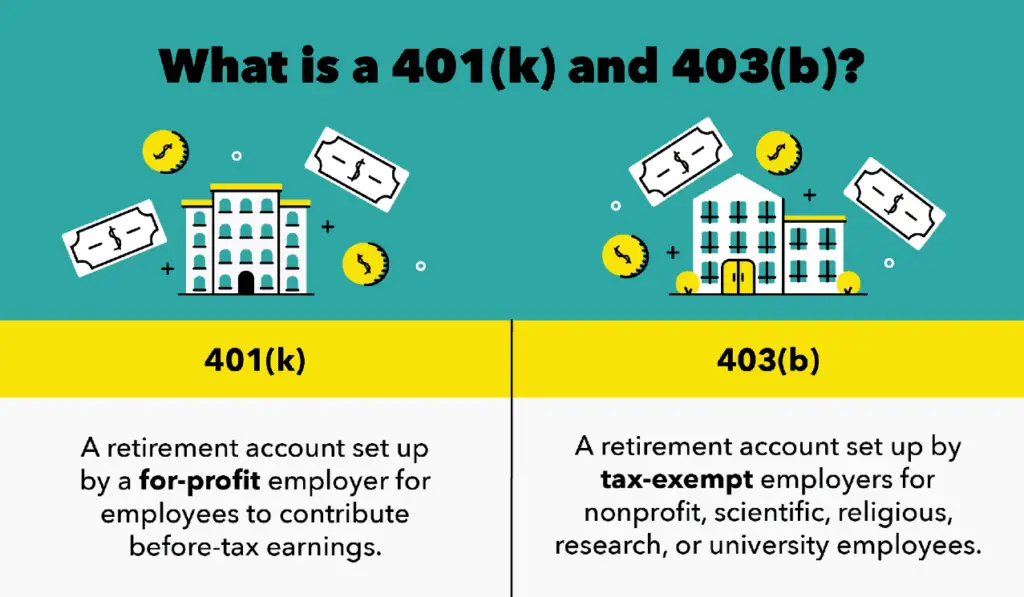
403 and 401 plans have a lot in common. You can use either one to chase down your wildest retirement dreams! The main difference is the type of employer who offers them. 401 plans are offered by private, for-profit companies, but 403 plans are offered by nonprofit organizations. Well unpack some other differences in a minute.
First, lets take a look at each plan.
The Secure Act And Annuities In 401 Plans
However, with the Setting Every Community Up for Retirement Enhancement Act, employees may see more annuity options offered in their 401 plans. This is because the SECURE Act eliminates many of the barriers that previously discouraged employers from offering annuities as part of their retirement plan options.
Additionally, under Section 109 of the SECURE Act, annuity plans offered in a 401 are now portable. This means that if the annuity plan is discontinued as an investment option, participants can transfer their annuity to another employer-sponsored retirement plan or IRA, thereby eliminating the need to liquidate the annuity and pay surrender charges and fees.
Also Check: Can I Take Money Out Of My Fidelity 401k
Whats The Difference Between 403 And 401
If you are not self employed, your primary retirement account will most likely be a 401 or a 403. While these plans are similar in some ways, there are some distinct differences as well, especially if youre moving from an employer that offers one to an employer that offers the other. Lets find out some more details.
Can I Convert Or Rollover These Plans To An Ira
Same. After leaving your employer, you can roll over some or all of your 401 or 403 plan to a traditional IRA. In some cases, depending on your costs and any plan restrictions in place from your administrator, transferring your money into an IRA might actually be better.
If your 401 or 403 is a traditional tax-deferred style setup, avoid converting or rolling it over to a Roth IRA. If you do, youll owe taxes on the entire amount that was converted. Whats worse, depending on how much money were talking, it could push you into one of the highest tax-brackets meaning that you would owe far more in taxes than youd ever otherwise owe. Avoid this option unless you absolutely know what youre doing.
Readers Who else also has one or both of these types of retirement plans? What the advantages and disadvantages that you have noticed between a 403 vs 401?
Don’t Miss: Why Choose A Roth Ira Over A 401k
Do I Get To Choose Which One I Want
Most workplaces that qualify to offer a 403b will do so because the administrative costs are lower. However, you arent able to open a 401k if your employer doesnt offer it. In other words, you dont get to choose which plan you want. At my first job, I had a 403b because I worked for a state hospital, which, as a government entity, was eligible for this plan.
Can You Also Make Ira Contributions
Same. In most cases, employees with either 401 or 403 plans can contribute to an IRA too. But take note that the IRS a number of special rules when it comes to who can contribute based on whether you participate in a retirement plan at work and what your income level is.
For example: If you contribute to both a 401 plan and an IRA, your ability to deduct this amount on your tax-return may be limited.
Roth IRA contributions are usually less restrictive since they are mainly restricted by how much you earn. If youre in doubt, check the official IRS rules or call a tax professional to know for sure.
Read Also: How To Know If You Have A 401k
Are They The Same Thing As A Pension
Same. Nope. Not at all. A pension is something totally different.
Pensions are older style plans where your employer pays you a pre-determined amount of money every month after you retire for the rest of your life . 401s and 403s were each created with the intentions of helping workers save more money for retirement IN ADDITION to receiving a pension.
Unfortunately pensions have gone the way of typewriters and VHS tapes towards extinction. To keep costs down, most organizations have shifted away from them. As a matter of fact, the EBRI reports that fewer than 2% of people in the private sector still participate in pension plans any more.
Basically, unless you happen to work someplace that still offers a pension, whatever you save for retirement yourself is all you will have.
Advantages Of 403 Plans:
- A 403 plan allows you to save on a tax-advantaged basis, deferring taxes on your income and any investment earnings or enjoying a tax-free benefit, depending on which plan you select.
- 403 employer contributions may vest faster than in 401 plans.
- If you are no longer with your employer, 403 rules may be more flexible than 401 early withdrawal rules.
- You can contribute more to a 403 plan each year than you can to an IRA.
Don’t Miss: What Is An Ira Account Vs 401k
Contribution And Withdrawal Similarities
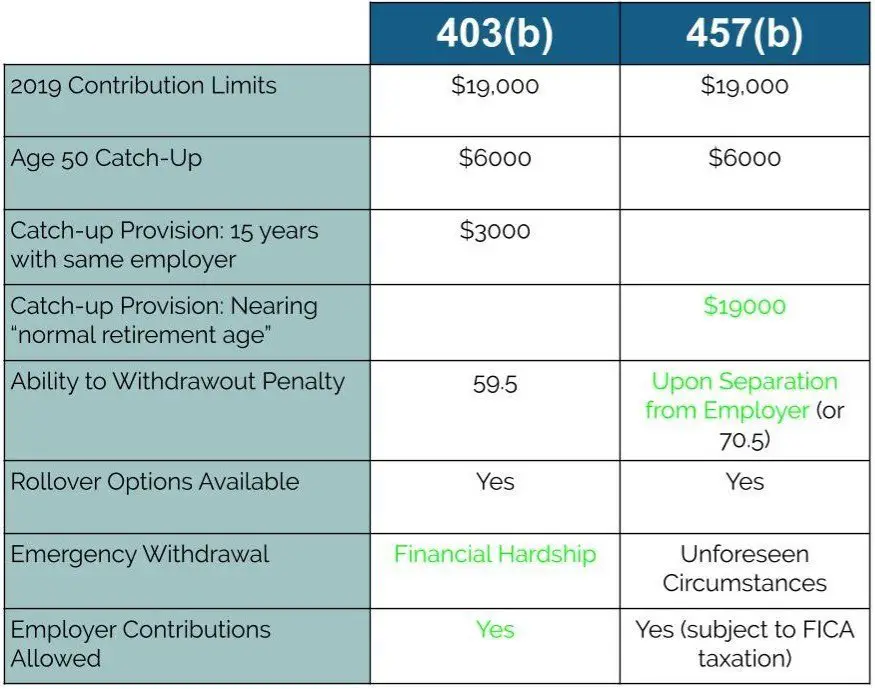
Both 401k and 403 plans are tax-advantaged retirement vehicles offered by employers. There are a number of methods for funding, and the one most people are familiar with is deferral into the plan directly from your paycheck. For 2021, 401k and 403 plans have the following deferral limits:
- Employees can contribute up to a maximum amount of $19,500
- For workers ages 50 and older, the contribution limit increases by $6,500, for a maximum deferral of $26,000 per year.
Some 401k and 403 plans are designed to allow the employer to make contributions as well. These can take the form of employer lump sum contributions at various intervals or matching where the employer contributes a certain amount on top of your own deferral. The total maximum contribution limit across employee deferrals and employer contributions for 2020 is $57,000, or $63,500 if over age 50.
Read More: When Can You Withdraw From Your 401k or IRA Penalty Free?
Plan Vs 401 Plan // Whats The Difference
When it comes to retirement planning, all the options available out there can get confusing. There are many plans out there, but do you really know the difference between a 401k, 403b, 457b, 401a, and all the others? You are not alone as most people have trouble when it comes to comparing all the different retirement plans that might be available. Luckily, we are here to help! If you are choosing between a 403b vs 401k, then you are in the right place. We will tell you everything that you need to know about both plans as well as the key differences between the two. Keep reading to learn more about these two plan types.
Read Also: How Do I Know Where My 401k Is
The 403b Plan The Basics
403 plans are very similar to 401 plans, except that where 401 plans are sponsored by for-profit businesses, 403 plans are for not-for-profit organizations that are tax-exempt under IRS Code 5013. That includes educational institutions, school districts, governmental organizations, religious organizations, and hospitals.
- Income Tax Treatment. Same as for the 401 plan.
- Contribution Limits. Same as for the 401 plan, except for the maximum allowable contribution provision below.
- Employer Matching Contributions. Same as for the 401 plan.
- Withdrawal Requirements. Same as for the 401 plan.
- Required Minimum Distributions . Same as for the 401 plan, except that 403 plans have a special allowance for plans that received pre-1987 amounts. If so, then distributions are not required until December 31 of the year in which the plan participant turns age 75 or, if later, April 1 of the calendar year immediately following the calendar year in which the participant retires.
- 403 Portability and Rollover Provisions. Same as for the 401 plan, except that a 403 plan can also be rolled over into a 401 plan of a new employer.
Legal Differences Between 403 And 401
The fact is that 403 has no compliance with the different regulations of the Employee Retirement Income Security Act . ERISA is the governing head controlling both the 401 and 403 plans. Every year, this is done to manage the highly compensated who receive disproportionate beneficiary amounts from the particular Plan.
In addition, investment funds must be registered as one of the official investment companies as per the Securities and Exchange Act of 1940. The only reason behind this, all the other exemptions fall under the long-standing Department of Labor Regulation. In this regulation, 4039 plans are not considered unless and until the employer is not funding the retirement scheme.
You May Like: Should I Roll My 401k Into An Annuity
How Do You Go About Choosing Between The Three Plans
In most cases, you wont have a choice as to which plan youll participate in.
That’s to say:
Your choice is determined by the type of employer you work for.
If its a private, for-profit corporation or business, youll most likely be offered the 401 plan. But if its a non-profit or government agency, you may be offered either the 403 or 457 plan.
However, a very limited number of government agencies offer a 401 in addition to either a 403 or 457 plan.
And in some cases you may have different plans with different employers.
For example, you may begin the year with a government agency that offers a 457 plan and end the year with a private corporation offering a 401 plan.
If you have an opportunity to participate in both plans, the maximum annual combination of contributions will be $57,000, or $63,500 if you are 50 or older. That includes your own regular contributions, catch-up contributions, and any employer matching contributions.
B Vs 401k: Structural Differences
In many respects, these two plans are similar in their structure and function. There are some notable differences, though. For example, 403b plans are not required to comply with many of the disclosure regulations found in the federal Employee Retirement Income Security Act . This Act governs most employer-sponsored retirement plans in the U.S.
This means that 403b plans are exempt from whats known as non-discrimination testing. Done annually, this test is designed to prevent management-level or highly compensated employees from receiving a disproportionate amount of benefits from a given retirement plan.
Don’t Miss: How To Transfer 401k Without Penalty
How We Make Money
The offers that appear on this site are from companies that compensate us. This compensation may impact how and where products appear on this site, including, for example, the order in which they may appear within the listing categories. But this compensation does not influence the information we publish, or the reviews that you see on this site. We do not include the universe of companies or financial offers that may be available to you.
Nonprofit Retirement Plan Cost Considerations
403s have historically been notorious for excessive fees. A recent feature in the New York Times explained, “The 403 accounts that many workers contribute to are not subject to the more stringent federal rules and consumer protections that apply to 401 plans.” This, in combination with the fact that many organizations don’t have a lot of options when it comes to 403 providers, means that many of the current 403 plans currently in existence offer employees a confusing set of high-fee funds.
Not all 403 plans have to be bad, and at Human Interest, we pride ourselves on offering a 403 that is on par with our 401 offerings, in the best interest of organizations and employees who do a lot of good for the world.
Related articles:
Also Check: How Do I Get My 401k
What Is A 403 Plan
A 403 plan is a type of retirement plan that can only be offered by qualifying tax-exempt employers. It’s also known as a tax-sheltered annuity, though money can be invested into both annuities and mutual funds. These plans enable employees to contribute pre-tax money from their earnings directly to their plan. That money is then invested in annuities or mutual funds that are likely to gain in value over time.
Earnings grow tax-deferred until you start taking dispersals. You need to be at least 59 ½ to begin to withdraw funds from a 403 without paying a penalty, unless you qualify for a special circumstance, such as financial hardship or disability.
403 plans are only offered by tax-exempt employers, such as 501 nonprofits, public schools, cooperative hospitals, and some religious organizations. The employer is the 403 plan sponsor and usually hires a provider to develop the options it will offer employees and to administer the plan itself.
Every plan is different and tailored to what the employer chooses to provide, such as the ability to take out loans or contribute after-tax dollars. You are generally eligible to participate in a 403 when your employment begins, though some employers set their own rules for eligibility and may opt to automatically enroll you in a plan.
Quick tip: If your 403 plan allows you to contribute after-tax dollars to a designated Roth account, you won’t have to pay taxes when you withdraw those funds.
