What Is A 401
A 401 is a retirement savings plan that many employers offer. You can invest a percentage of your pay or a specific amount each month. And you make your investments with pretax money, meaning that whatever you invest is taken out of your paycheck before your income is taxed.
A 401 is named after the subsection of the IRS code that talks about retirement plans. The money you invest can go into several different types of mutual funds, depending on your plan.
Certain businesses dont offer a 401 plan, but they might offer something like it:
- 403 This plan is like a 401 for tax-exempt organizations like public schools, hospitals or religious groups.
- 457 This plan is offered by state and local governments and some nonprofits.
A huge plus of 401, 403 and 457 plans is that your employer can match your investment up to a certain amount. Matching isnt required by the government, so not all employers offer it. If your company offers a 401, find out if your employer offers a match so you can make the most of your investing dollars. Were talking about free money, everybody!
And heres some peace of mind: The money you invest is all yours. You can roll over your 401 account to an IRA if the company goes under or if you decide to move on.
You Can Withdraw Your Contributions From Either Plan At Any Time Tax
There is another unique feature of Roth accounts, and it applies to both Roth IRAs and Roth 401s. That is, you can withdraw your contributions from a Roth plan at any time, without having to pay either ordinary income tax or the 10% early withdrawal penalty on the distributions.
This is in part because Roth IRA contributions are not tax-deductible at the time they are made. But its also true because of IRS ordering rules for distributions that are unique to Roth plans. Those ordering rules enable you to take distributions of contributions, ahead of accumulated investment earnings.
There is some difference in exactly how early distributions are handled among Roth IRAs and Roth 401s.
Early distributions from Roth IRAs enable you to first withdraw your contributions which were not tax-deductible and then your accumulated investment earnings once all of the contributions have been withdrawn. This provides owners of Roth IRAs with the unique ability to access their money early, without incurring tax consequences.
With Roth 401s the contribution portion of your plan can also be withdrawn free of both ordinary income tax and early withdrawal penalties. But since theyre 401s, theyre also subject to pro-rata distribution rules.
If you have a Roth 401 that has $20,000 in it, comprised of $14,000 in contributions and $6,000 in investment earnings, then 30% of any early distribution that you take, will be considered to represent investment income.
What If I Leave My Job
If you leave your employer, you can roll your pretax retirement plan balance into an Individual Retirement Account and your Roth balance into a Roth IRA. You also may have the option of rolling your account into your next employers retirement plan. Consider the pros and cons of each before deciding whats right for you. See if an IRA is right for you.
Note: Similar concepts about the timing of tax savings apply to Roth and traditional IRAs.*This is applicable if you meet certain conditions.
- Fund Asset Size$} M
- Average Market Cap$} M
- Price/Book Ratio}x
- Change from Previous Day}0
- YTD as of }}0
- YTD as of }}0
- 1 Month}0
- Year End } unit value$}
- Daily as of } unit value$}
Don’t Miss: What Is My Fidelity 401k Account Number
Regular 401k & Ira: The Undeniable Math To Avoid The Roth
If you are using the Safari browser, turn off “content blockers” for a better font experience.
Retirement planning does not come easy for most people and there are a plethora of choices to make in the process. If you have ever asked, Should I do a Roth or traditional 401k, this article is for you.
This article is not about discussing whether you should pick an Individual Retirement Account versus a 401. Instead, its about whether you should pick the Roth or traditional style of either account type.
The obvious question is Which account style leads to more money? And the answer we will prove herein is that its the traditional 401k or standard IRA, and not the Roth account style, contrary to popular opinion and finance gurus.
Tip : Tax Rateshigher Now Or Later
Retirement accounts like 401s, 403s, and IRAs have a lot in common. They all offer tax benefits for your retirement savingslike the potential for tax-deferred or tax-free growth. The key difference between a traditional and a Roth account is taxes. With a traditional account, your contributions are generally pretax. They generally reduce your taxable income and, in turn, lower your tax bill in the year you make them. On the other hand, you’ll typically pay income taxes on any money you withdraw from your traditional 401, 403, or IRA in retirement.
A Roth account is the opposite. Contributions are made with money that has already been taxed , and you generally don’t have to pay taxes when you withdraw the money in retirement.1
This means you need to choose between paying taxes now or in retirement. You may want to get the tax benefit when you think your marginal tax rates are going to be the highest. In general:
Also Check: How Do I Invest In My 401k
Roth 401 Vs Roth Ira: Whats The Difference
Eric is currently a duly licensed Independent Insurance Broker licensed in Life, Health, Property, and Casualty insurance. He has worked more than 13 years in both public and private accounting jobs and more than four years licensed as an insurance producer. His background in tax accounting has served as a solid base supporting his current book of business.
Traditional And Roth 401 Plans
Individuals who want to save for retirement may have the option to invest in a 401 or Roth 401 plan. Both plans are named for the section of the U.S. income tax code that created them. Both plans offer tax advantages, either now or in the future.
With a traditional 401, you defer income taxes on contributions and earnings. With a Roth 401, your contributions are made after taxes and the tax benefit comes later: your earnings may be withdrawn tax-free in retirement.
You May Like: Can I Transfer My Ira To My 401k
Roth 401 And Roth Ira Early Withdrawal
Although a Roth 401 account is funded with after-tax dollars, it is not immune to taxes and penalties. Understanding the rules regarding withdrawals is important if you want to avoid losing part of your retirement savings. Contributions and earnings in a Roth 401 can be withdrawn without paying taxes and penalties if youre at least 59 and a half years old and you meet the five year rule. Other exceptions include being permanently and totally disabled. You can also use up to $10,000 for a first-time home purchase without penalty or taxation.
Early Withdrawal of Roth Account Contributions
All withdrawals are not the same. Your Roth IRA contribution can be used in an emergency. If you need to take an early withdrawal from a Roth account contributions come out first. This is a nice move by the IRS to make things easier for you. When youre just tapping into your contributions, you dont have to worry about taxes, unless you pull out more than youve contributed.
Early Withdrawal of Roth Account Earnings
Things get more complicated when you start tapping into earnings. You can be taxed and have to pay a 10% penalty for early withdrawals on your Roth account earnings. However, there are some circumstances where you will not have to pay the 10% penalty, but still need to pay taxes. These special circumstances include:
Pros And Cons Of The Roth 401 And Roth Ira
The table below shows the pros and cons of both account types.
| Account Type |
|---|
|
It’s worth noting that you might be able to avoid the required withdrawals from a Roth 401 by converting it to a Roth IRA.
Recommended Reading: What Should I Do With My Old Company 401k
Heres What To Do On Roth 401 Vs Roth Ira:
-
If your 401 investments are pricey, contribute just enough to get the company match, and then proceed directly to a brokerage to open a Roth IRA.
-
If your 401 offers low-cost mutual funds, then youre ready to check out our chart to decide whether the Roth IRA or Roth 401 makes the most sense for you. Or, if youre ready to maximize your retirement savings, go ahead and contribute to both.
Ira Or Traditional Ira
An IRA isan individual retirement arrangement and is an account that has somesimilarities to a 401 in terms of the contributions. When comparing a 401to an IRA, one of the first things to note is that contributions to both typesof accounts are made on a pre-tax basis so that they reduce your income taxbill during the tax years in which they are made. Funds in both accounts areable to enjoy tax-deferred growth. You will pay taxes when you begin takingdistributions to either a 401 or an IRA.
If you have an IRA, you hold it entirely. You will notreceive matching contributions to the account. Since you are the sole owner ofan IRA, you can choose which financial institution or brokerage firm will holdit. Since you will own the plan, choose your own investments, and pick the firmthat will hold it, you should know how much your IRA costs you in terms offees.
When you compare a 401 vs. a traditional IRA, you willsee that IRAs have significantly lower annual contribution limits. If you areunder age 50, you can contribute a maximum of $6,000 per year. If you are age50 or older, you can contribute an additional $1,000 per year for a total annualmaximum contribution of $7,000. You can begin taking distributions when youturn age 59 1/2, and you will have a required minimum distribution beginning atage 70 1/2. If you withdraw funds from your IRA before you reach age 59 1/2,you will be assessed an early withdrawal penalty of 10 percent unless anexception applies.
Don’t Miss: How To See How Much Is In My 401k
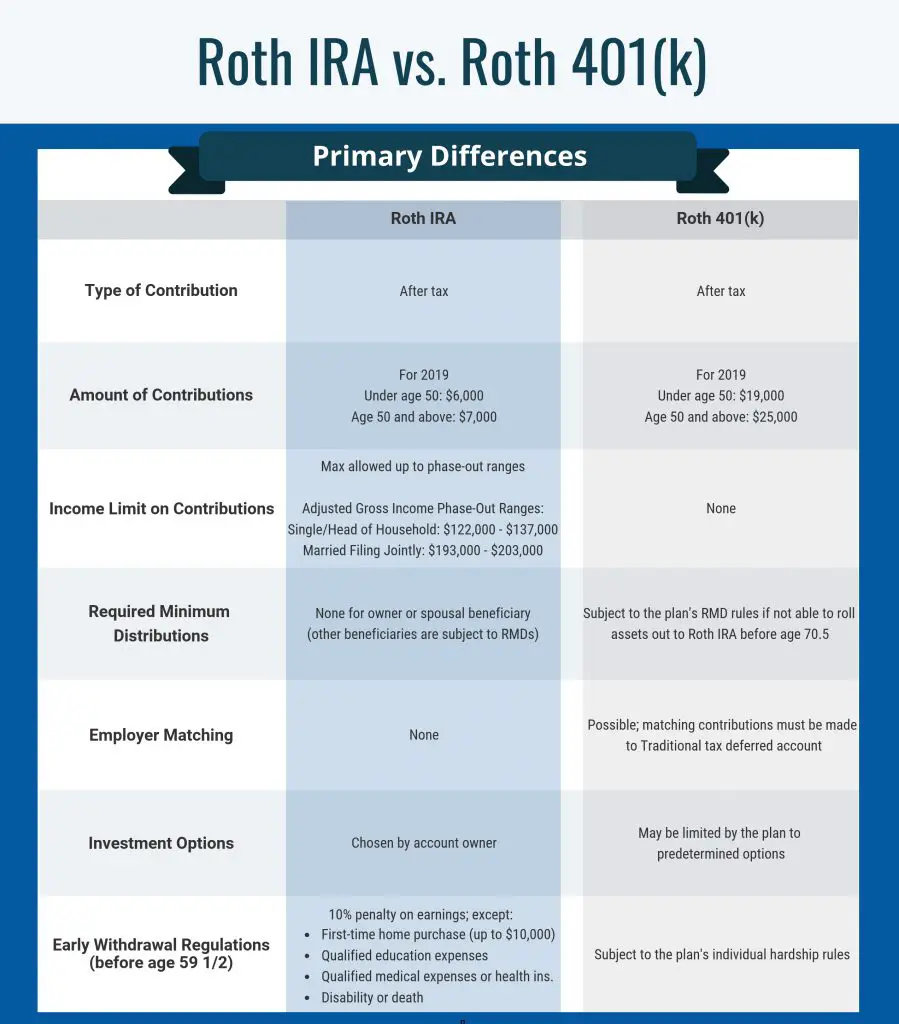
Key Differences Between A Roth 401 And A Roth Ira
- Roth 401 accounts and individual retirement accounts allow for after-tax savings. Money withdrawn during retirement is tax-free.
- However, there are some big differences between Roth 401 plans and Roth IRAs.
- They include contribution limits, income qualification and required minimum distributions.
Roth accounts are after-tax accounts with unique benefits for retirement savers.
Namely, investments grow tax-free, and withdrawals aren’t subject to tax during one’s retirement years. But there are some key differences between Roth savings in a 401 plan and in an individual retirement account.
Here are some of the biggest.
Roth Conversions May Not Pay Off Until Age 90 For Most

Roth conversions almost always work out in a client’s favor, but not necessarily for the reasons that advisers often recommend them, according to an academic study published this week. Contrary to conventional wisdom, tax-rate changes — up, down, or flat — have a minimal effect on the long-term financial benefits from converting a traditional IRA or 401k to a Roth account, Edward McQuarrie, professor emeritus at Santa Clara University, wrote in a recent paper. Instead, the overarching factor that gives Roth conversion an edge, given enough time, is compounding, McQuarrie found.
Also Check: How To Transfer My 401k To My Bank Account
How Does It Work
The funds in a Roth IRA grow without being taxed. Withdrawals that are taken after age 59 1/2 from accounts at least five years old are tax-free.
Many people dont have to pay any income tax on the investment growth they accumulate in a Roth IRA.
Your contributions help, but its the power of compounding that does the heavy lifting when it comes to building wealth with a Roth IRA.
Your account has two funding sources: contributions and earnings. The former is the most obvious source of growth, but the potential for dividends and the power of compounding can be even more important.
Read: What is Thematic Investing? How it Works, Pros and Cons
How Are They Different
| Employers provide a 401 to employees as a benefit | An IRA is an individual retirement account, so it belongs to you individually |
| Lowers your taxable income because most 401 contributions are made before taxes are taken out | Your traditional IRA contributions are made from your taxable earnings, you are then permitted to deduct the contributions from your income in certain situations |
| The employer selects the investment options offered in the plan | Typically offers a wider range of investment options than a 401 |
| The employer may match up to a certain percentage of your contribution | Isnt tied to your employer, so you dont get a match on your contributionhowever, you have more control and flexibility when and how you contribute |
| You may be able to roll over an old 401 from a previous job into the 401 at your current job | You can roll multiple outside accounts like old 401s or other IRAs into one IRA to simplify your savings |
Also Check: How To Cash Out Nationwide 401k
The Rising Tide Of The Roth 401k
Many employer-sponsored retirement plan participants are conflicted in deciding which type of account is best for their 401k contributions: traditional or Roth? Often having no idea which is best for their situation, they need the help of an advisor. You can advise them with confidence if you know just two things.
Roth Ira Vs : What Are The Major Differences
The main difference between a Roth IRA and 401 is how the two accounts are taxed. With a 401, you invest pretax dollars, lowering your taxable income for that year. But with a Roth IRA, you invest after-tax dollars, which means your investments will grow tax-free.
Okay, folks, does anybody else feel like theyve been drinking water from a firehose? That was a lot of information! Lets review the main differences between the Roth IRA and the 401 so you can easily compare their features:
|
Feature |
|
|
Penalties for withdrawals before 59 1/2. |
Penalties for withdrawals before 59 1/2. |
Recommended Reading: How Much Can I Put In My 401k Per Year
Roth 401 & Roth Ira Faqs
At what age should I stop contributing to my Roth IRA?
There is no age limit. You can contribute to your Roth IRA until death if you choose to.
Can you lose money in a Roth IRA?
Yes, a Roth IRA is a vehicle that holds investments. If your investments lose value you will lose money.
Can I max out my 401 and Roth 401?
Theoretically no. Your total contribution would be divided between both, so neither one would technically be maxed out. Aggregate contributions to 401 and Roth 401 are capped at $19,500 .
How much should I put in my Roth IRA monthly?
That depends on your retirement goals. A good financial plan will lay that out for you.
How can I withdraw from my Roth IRA without penalty?
All contributions can be withdrawn tax and penalty-free. Earnings, however, will be taxed and penalized if you have not met the five-year rule and they are not used for a qualified exception.
When can I take money out of my Roth 401 without penalty?
You are free to take any contributions out of your Roth 401 without penalty at any time. Only earnings will be subject to penalty.
Who qualifies for Roth 401?
Anyone who works for an employer that offers a 401 to their employees qualifies for a 401.
Which Is Best For Your Retirement Goals
First things first: You don’t have to choose between a Roth IRA and a Roth 401. You can contribute to both. This can be the best option if your employer offers a match but you’d prefer a broader choice of investment options than a Roth 401 provides. In this scenario, you’d want to contribute enough to get the match and then put the remainder of your retirement funds into a Roth IRA until you hit the contribution limits.
Unfortunately, not everyone has a choice of Roth accounts. If your workplace doesn’t offer a Roth version of its 401, the only way for you to get the benefits of a Roth is to contribute to a Roth IRA.
On the other hand, if your income is too high for you to contribute to a Roth IRA, a Roth 401 may be your only choice if you prefer to take tax-free withdrawals from your retirement account rather than make pre-tax contributions to it.
If your employer does not offer a match and you’re eligible for both a Roth 401 and a Roth IRA, you’ll need to weigh the pros and cons of each account type. If you’d prefer not to worry about RMDs and/or want more investment choices, opt for a Roth IRA. But if you would rather have the convenience of a workplace account and don’t mind a more limited choice of investment options, a Roth 401 is your best bet.
Read Also: What Should I Invest In 401k
Compared To A Roth 401
A traditional 401 and a 401 Roth account haveseveral similarities. Like a traditional 401, the Roth 401 limits are$19,000 per year if you are under age 50 and $25,000 per year if you are olderthan age 50. The higher Roth 401 contribution limits after age 50 arebecause of catch-up contributions of an additional $6,000 per year.
Both types of accounts have required minimumdistributions when you reach age 70 1/2. However, a Roth 401 differs in whenyou will be assessed taxes. Since the contributions are made after tax, youwill not pay taxes when you take disbursements.
When you compare a Roth 401 vs. a Roth IRA, you willnotice that both have contributions made on an after-tax basis, and neitherwill subject you to taxes when you take distributions. However, a Roth 401vs. a Roth IRA has higher annual contribution limits. The Roth 401contribution limits are the same as the contribution limits of a traditional401. Another difference is that a Roth 401 has requiredminimum distributions beginning at age 70 1/2 while a Roth 401 does not haveany required minimum distributions.
