How Does A Safe Harbor 401 Work
The IRS can reject a retirement plan contribution if it believes it’s excessive. If the employer doesn’t fix things, the plan could lose its tax-qualified status. One way to fix a plan is for the maximum allowed contribution to be lower. This would put higher-paid workers in line with those who aren’t fully active. The other is to recast the excess contributions of highly paid workers as taxable income.
If a plan loses its tax-qualified status, it costs you or the employee. You would owe federal and state income tax as well as Social Security, Medicare, and Federal Unemployment taxes. Workers could not roll over plan assets to other eligible retirement plans. Plus, there’d be a 10% excise tax on the excess contribution.
It might raise a flag for the IRS if you’re a business owner and your 401 has low adoption rates or saving rates among rank-and-file workers.
A long vesting schedule isn’t allowed with safe harbor plans. Contributions are fully vested when they’re made. The company must give all workers instant ownership. That includes those who leave or are fired during the year.
You have more options with a safe harbor plan. You can design your safe harbor plan to limit any matching contributions to those employees who defer compensation. You can also contribute for all workers. That includes those who don’t pay into their own plans.
Plans can contribute in one of three ways:
You Can Also Choose A Roth 401
Many 401 plans give participants the option to choose a Roth 401. With a Roth 401, you make contributions to your plan with after-tax income, meaning the contributions do not reduce your taxable income. Like a Roth individual retirement account , you pay no income taxes on qualified distributions, such as those made after the age of 59 ½ .
Choosing a Roth 401 can make sense if you believe you will be in a higher tax bracket when you retire than you are today. For many young earners who are just beginning their careers, lower income levels and tax brackets could make a Roth 401 a great choice.
There is nothing forcing you to choose between either a traditional 401 or a Roth 401you can make contributions to both kinds of 401 plan, if your employer offers them. Consider speaking with a tax professional or a financial advisor when deciding between a traditional or a Roth 401, or dividing your contributions between both types.
How Muchcan I Contribute To My 401k
Maximum contribution limits are revised regularly, which helps you to keep pace with inflation and wage growth as you invest in your 401k.
Currently, the contribution limit for individual contributions is $19,000 per year, up from $18,500 in 2018.
In most cases, this contribution limit applies to all of your defined contribution accounts combined. For example, if you also have a 403b account, the $19,000 limit applies to both accounts combined.
If you have a 401k and you have a traditional IRA, havingboth types of accounts can affect the deductibility of your IRA contributionsbut you can contribute to both accounts up to the individual limits of eachaccount type.
The IRS also allows additional 401k catch-up contributions for those nearing retirement age.
Currently, you can contribute up to an additional $6,000 to your 401k if you are 50 or older.
In many cases, employers offer matching contributions as well. The IRS provides a separate limit that applies to the total of your own contributions and employer contributions.
Currently the annual defined contribution limit is $56,000 annually. Because 401k contributions are handled as payroll deductions, you also cant contribute more than you earn.
For example, if youre working part time earning $15,000 per year, you wont be able to utilize the full $19,000 annual limit because your earnings are below the limit.
You May Like: How Much Can You Put In Your 401k A Year
Make It Easy To Enroll In Your Plan
The quick enrollment feature allows employees to sign up for a retirement plan in four clicks. When you integrate payroll, you can easily see who is eligible for your chosen retirement plan. This means you don’t have to track eligibility separately, saving you time to focus on your business.
Rmds For $10 Million Accounts
Now, RMDs for account homeowners are tied to age as a substitute of wealth. Roth IRA house owners also are not matter to these distributions beneath existing regulation.
The Dwelling legislation would insert to all those regulations, inquiring wealthy savers of all ages to withdraw a substantial share of aggregate retirement balances every year. Theyd perhaps owe profits tax on the money.
The method is sophisticated, based on factors like account size and variety of account . Heres the basic premise: Accountholders have to withdraw 50% of accounts valued at a lot more than $10 million. More substantial accounts will have to also attract down 100% of Roth account size above $20 million.
The distributions would only be expected for folks whose income exceeds $400,000. The threshold would be $450,000 for married taxpayers submitting jointly and $425,000 for heads of house.
The provision would get started just after Dec. 31, 2028.
Individuals with hundreds of thousands of pounds in retirement savings would possible change their fiscal plans to circumvent the rules effect if they are adopted, Keebler reported.
There may well be folks by now at $6 million who could determine not to place a lot more income into their IRAs, but into lifestyle coverage or other statutory tax shelters, Keebler explained.
You May Like: Can You Transfer Your 401k
How To Invest In A 401 Plan
It’s easy to get a 401 if you have a job, as you simply sign up through your employer.
However, not all employers provide access to this retirement savings and investment plan. If your employer falls in this category, all is not lost. You can still get the tax benefits offered by a 401 plan by making your contributions through an individual retirement savings account.
When signing up for your 401, you will need to choose your specific investments from the selection offered by your employer.
The selection could include some of the following investments:
- Company stock
- Stock and bond mutual funds
- Target-date funds comprising a mix of stocks and bonds
- Guaranteed investment contracts from insurance companies
Plans For Certain Small Businesses Or Sole Proprietorships
The Economic Growth and Tax Relief Reconciliation Act of 2001 made 401 plans more beneficial to the self-employed. The two key changes enacted related to the allowable “Employer” deductible contribution, and the “Individual” IRC-415 contribution limit.
Prior to EGTRRA, the maximum tax-deductible contribution to a 401 plan was 15% of eligible pay . Without EGTRRA, an incorporated business person taking $100,000 in salary would have been limited in Y2004 to a maximum contribution of $15,000. EGTRRA raised the deductible limit to 25% of eligible pay without reduction for salary deferrals. Therefore, that same businessperson in Y2008 can make an “elective deferral” of $15,500 plus a profit sharing contribution of $25,000 , andâif this person is over age 50âmake a catch-up contribution of $5,000 for a total of $45,500. For those eligible to make “catch-up” contribution, and with salary of $122,000 or higher, the maximum possible total contribution in 2008 would be $51,000. To take advantage of these higher contributions, many vendors now offer Solo 401 plans or Individual plans, which can be administered as a Self-Directed 401, permitting investment in real estate, mortgage notes, tax liens, private companies, and virtually any other investment.
You May Like: Can You Convert A Roth 401k To A Roth Ira
What Are The 401k Maximum Contribution Limits
The max contribution limits have been rising year over year. As of this year, the maximum contribution limit is $19,500 whereas the maximum catch-up limit is $6,500. The catchup limit is for those over the age of 50.
The contribution limits depend on the type of plan that you choose. It is also influenced by factors such as government guidelines and the amount of money that you earn in the first place.
Generally, your employer or organizational policies will determine the maximum contribution limit for your plan. This will be expressed as the percentage of salary that you can divert towards retirement savings. You will be informed about the limit at the time of agreement.
For instance, if you are allowed to contribute 5% of your salary and you earn $20,000 pre-tax, the maximum contribution limit for your 401k will be $1,000.
Given the rising cost of living in the last decade, the government has increased the maximum contribution limit for 401k plan by $500 every year since 2010.
How To Choose The Right Plan For You
The 401, the 403 and the 457 plans are similar your employer offers the one designed for your type of organization. If you are self-employed, a small-business owner, or the employee of a small business, a SEP plan or a SIMPLE IRA are alternative ways to set aside money income tax-deferred for retirement. In some cases, only your employer can contribute to a 401. All plans let you contribute additional money into your own Traditional IRA or Roth IRA. However, If you are an active participant in a plan, your contribution to an IRA may be limited.
This material is provided for general and educational purposes only it is not intended to provide legal, tax or investment advice. All investments are subject to risk. When redeemed, an investment may be worth more or less than the original amount invested. Neither Voya nor its affiliated companies provide tax or legal advice. We recommend that you consult an independent tax, legal, or financial professional for specific advice about your individual situation.
The information herein is not intended to be used, and cannot be used by any taxpayer, for the purpose of avoiding tax penalties. Taxpayers should seek advice based on their own particular circumstances from an independent tax advisor.
Financial advisors and Financial Planning Consultants are Investment Adviser Representatives and Registered Representatives of, and offer securities and investment advisory services through Voya Financial Advisors, Inc .
Also Check: What Happens To 401k When You Die
How Much Of My Salary Can I Contribute To A 401 Plan
The amount that employees can contribute to their 401 Plan is adjusted each year to keep pace with inflation. In 2020 and 2021, the limit is $19,500 per year for workers under age 50 and $26,000 for those aged 50 and above.
If the employee also benefits from matching contributions from their employer, then the combined contribution from both the employee and the employer is capped at the lesser of $58,000 or 100% of the employees compensation for the year.
Take Advantage Of A 401k Plan For Your Retirement
The biggest advantages of using a 401k for retirement savings are the high contribution limits and the employer matching contributions.
If your employer offers matching contributions, that alone is often enough reason to participate in the 401k plan because matching contributions are a guaranteed return on investment.
If your employer doesnt offer matching contributions and you cant afford to make a large contribution each year, an IRA may be a better choice in the interim because fees are often lower and youll have a wider choice of investments.
Of course, you might be able to use both types of accounts and diversify your retirement investments while giving yourself more investment choices.
Don’t Miss: How Do I Find Out Where My Old 401k Is
How 401 Plans Work
The 401 plan was designed by Congress to encourage Americans to save for retirement. Among the benefits they offer is tax savings.
There are two main options, each with distinct tax advantages:
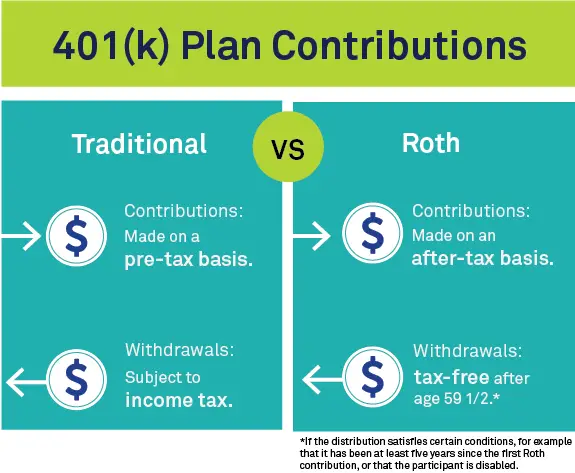
- A traditional 401 is deducted from the employee’s gross income. The employee’s taxable income is reduced by that amount and can be reported as a tax deduction for that year. No taxes are due on the money paid in or the profits it earns until the employee withdraws it, usually after retiring.
- A Roth 401 is deducted from the employee’s after-tax income. The employee is paying income taxes on that money immediately. When the money is withdrawn during retirement, no additional taxes are due on the employee’s contribution or the profits it earned over the years,
Not all employers offer the option of a Roth account.
If the Roth is offered, the employee can pick one or the other or a mix of both, up to annual limits on their tax-deductible contributions.
Why Save In A 401

Contributing to a 401 plan can help participants prepare for retirement. By participating in their companys 401 plan, employees can take advantage of matching contributions from their employer, enjoy preferential tax treatment on both pretax and post-tax contributions, harness the power of compounding, and gain access to a wide range of investment options. Check out this article for even more reasons to get started today.
1 Limits are for 2019 and can be subject to change annually. 2 Ordinary income taxes are due on withdrawal. Withdrawals before the age of 59½ may be subject to an early distribution penalty of 10%. 3 This is a hypothetical illustration used for informational purposes only. The marginal tax bracket used is 25%. This lump-sum, after-tax figure doesnt account for the possible change in tax bracket that might occur due to a lump-sum distribution of the taxable amount, nor does it take into effect any applicable tax penalties. There is no guarantee that the results shown will be achieved, and the assumptions provided may not be reflective of your situation. 4 Only applies to qualified distributions, which means the money is withdrawn when you are at least 59½ years old, or on death or disability, and youve held Roth contributions in your account for at least five years .
You May Like: Should I Rollover 401k To New Employer
Annual 401 Contribution Limits
For 2020 and 2021, the maximum an employee can contribute to a 401 is $19,500. If youre 50 or older, you can deposit an extra $6,500 in catch-up contributions, for a combined contribution of $26,000. These limits apply to all 401 contributions, even if you split them between pre-tax and Roth contributions, or you have two employers in a year and thus two separate 401 accounts.
About a fifth of employers also allow after-tax, non-Roth contributions. In such cases, a combined employee and employer contribution limit applies. In other words, your employers contributions, combined with your pre-tax, Roth and after-tax contributions, cant exceed this limit. For 2020, that combined limit is $57,000, or $63,500 for those 50 or older. For 2021, the total limit rises to $58,000 or $64,500 for those 50 or older. Unlike Roth contributions, these extra after-tax savings grow tax deferred, but not tax free.
The contribution limits are updated as frequently as annually based on inflation, so its important to check back to see if you can increase your contribution if youve been contributing the maximum.
How Do 401 Required Minimum Distributions Work
Holders of both traditional 401s and Roth 401s are required to take RMDs. The amount of your RMDs is based on your age and the balance in your account. As the name suggests, an RMD is a minimumyou can withdraw as much as you wish from the account each year, either in one lump sum or in a series of staggered withdrawals. As noted above, RMDs from a traditional 401 are included in your taxable income, while RMDs from Roth 401s are not.
You May Like: What Happens To My 401k If I Switch Jobs
What Happens To Your 401 When You Switch Jobs
Fortunately, a 401 offers portability, so you dont need to be stuck in a former plan if you dont like it. Workers have a few options for dealing with their old 401 after leaving a company:
- Roll it over into an IRA.
- Keep the assets in the former employers plan, if permitted.
- Roll it over into a new employers plan, if permitted.
You may also have the option of taking a cash distribution, or lump sum, but youll probably get hit with penalties and taxes if youre not at least of retirement age.
Whichever path you choose, its important to understand the benefits and limitations of each option according to your unique financial situation, Golladay says.
Taking an early distribution could be disastrous for your retirement, and more than half of Americans say they are behind in saving for retirement, according to a Bankrate survey.
Heres what you can do with your 401 if you switch jobs, either voluntarily or involuntarily.
How Long Will My 401k Last
How long your retirement savings lasts depends on the amount you have saved as well as the annual return on your remaining funds and the rate of inflation.
A $500,000 nest egg will last 21 years if youre earning 7% on the remaining balance and withdrawing $35,000 per year.
This example assumes a 3% inflation rate.
A million-dollar 401k balance bumps your retirement income up to $70,000 for 21 years, assuming the same rate of return and inflation rate.
Also Check: Can You Have A Solo 401k And An Employer 401k
How Much Does It Cost To Offer A 401 To My Employees
401 fees can be tricky. In many instances, fees are deducted from participant accounts and are not very transparent. There are typically two kinds of 401 fees: investment and plan administration expenses:
- Investment expense: The investment expense ratio is the revenue the investment company collects to manage the fund . Investment expense is generally not visible as a fee to the employer or employees because the fee is netted from the funds return.
- Plan administration fee: The plan administration fee is the fee the provider collects for basic administrative services such as plan record keeping, accounting, legal and trustee services.
