The Differences Between 401 And 403 Plans
The biggest difference between 401 and 403 plans is the eligibility requirements for participants. Employees of for profit organizations are able to contribute to 401 plans, while employees of tax-exempt organizations are permitted to save using a 403 plan. Employers are responsible for setting up retirement savings plans, and those that choose to offer company-sponsored plans select the most appropriate option based on their employee population. This simplifies the decision for workers, as they will be guided into the correct retirement plan by their employers.
Both 401 and 403 plans can choose investment managers to manage the retirement accounts of their employees. Nonprofit companies may also permit their 403 plans to be in the form of annuity contracts, which are managed by insurance companies. With this option, investors contribute to the annuity in exchange for guaranteed income upon retirement. 403 plans can also invest in retirement income accounts, which operate in a similar manner to annuities. Costs for 401 and 403 plans vary depending on the type of investment and the financial institution handling the investments.
K Vs 403b Retirement Plans
The difference between 401K and 403B retirement plans is that 403b is executable only if you are a part of any non-profitable organization like a hospital or an educational institute. However, a 401k retirement plan is applicable to all the employees whose organization is profitable and has its own set of advantages.
| The 401k retirement plan is limited by a lot of mutual funds investment opportunities. | The 403b retirement plan is limited by majorly different annuity options. |
Special Mac Rule With 403 Plans
Those with 15 years of service to an employer can then add another $3,000 to their annual contribution limit, depositing a potential $22,500 per year . This is called the maximum allowable contribution, or simply MAC.
Unfortunately, just because MAC is allowed under the IRS code does not mean the employer has to honor it. They have to include it in their plan document for it to go in effect. I had a client that met the 15-year requirement but since she was one of the only ones that did, her employer wasnt aware of the MAC rule and didnt feel the need to include it in their plan.
Read Also: Can I Borrow From My 401k Without Penalty
Vs 401 Comparison: Similarities
As weve stated, 403s and 401s share a lot of similarities. At a glance, those similarities include:
-
Their Names: Both plans are named for their corresponding sections of the IRS code.
-
General Contribution Limits: Under both plan types, employees can contribute up to $19,500 in 2021. Older participants can make catch-up contributions.
-
Employees can have their contributions automatically removed from their paychecks and dont have to pay income taxes on pre-tax contributions.
-
The accounts are both tax-deferred, which means the contributions and earnings grow without being taxed until you start making withdrawals.
-
Penalties: Under both plan types, participants may receive penalty fees for withdrawing money too early or not taking RMDs once they reach 72 years old.
The Similarities Between 401 And 403
Aside from their differences, both accounts are set up to aid employees in retirement savings. Heres how:
- Contribution limits: Both accounts cap your annual contributions at $19,500. In the event you contribute over this limit, your earnings will be distributed back to you by . If youre under your retirement contributions by the time youre 50 years old, youre allowed to make catch-up contributions. This means that, if youre eligible, you can contribute $6,500 more than the yearly contribution limit.
- Withdrawal eligibility: You must be at least 59.5 years old before withdrawing your retirement savings. In the case of an emergency, you may be eligible for early withdrawal. However, you may be charged penalties, taxes, and fees for doing so.
- Employer matching: Both retirement account options allow employers to match your contributions, but are not required to. When starting your retirement fund, ask your HR representative about potential benefits and employer matching.
- Early withdrawal penalties: If you choose to withdraw your retirement savings early, you may be penalized. In most cases, you need a valid reason to withdraw your funds early. Eligible reasons may include outstanding debt, bankruptcy, foreclosure, or medical bills. In addition, you may be charged a 10 percent penalty fee, taxes, and other fees. During a downturned economy, as weve seen with the COVID-19 pandemic, fees may be waived.
Recommended Reading: Can 401k Be Transferred To Roth Ira
The Differences Between 401s And 403s
With all of the similarities between the two retirement accounts, there are some key differences to be aware of.
While 403 plans are eligible to provide employer matches to their employeesâ contributions, most employers are donât offer to match contributions, so they do not lose ERISA exemptions. In contrast, 401 plans provide an employer match at a far high rate than 403 plans.
However, vesting occurs much quicker with 403 plans than with 401, with many 403s offering immediate vesting to its employees.
Additionally, 403 plans offer an additional catch-up bonus for employees even if they are under 50. Employees who have been with a company for 15 years can begin making catch-up bonuses of $3,000 per year. Catch-up bonuses towards 403s are capped at a $15,000 lifetime amount.
Lastly, the investment options vary significantly between 401s and 403s. While 401s offer about 19 different investment options on average, 403 offer only a few mutual funds that participants can choose from. 403 plans prominently feature annuities, while 401 plans tend to offer an array of mutual and index funds. This is because insurance companies often administer 403 plans, whereas 401s are usually administered by mutual fund or investment companies.
Tags
The Differences Between 401 And 403
Both a 401 and 403 are similar in the way they operate, but they do have a few differences. Here are the biggest contrasts to be aware of:
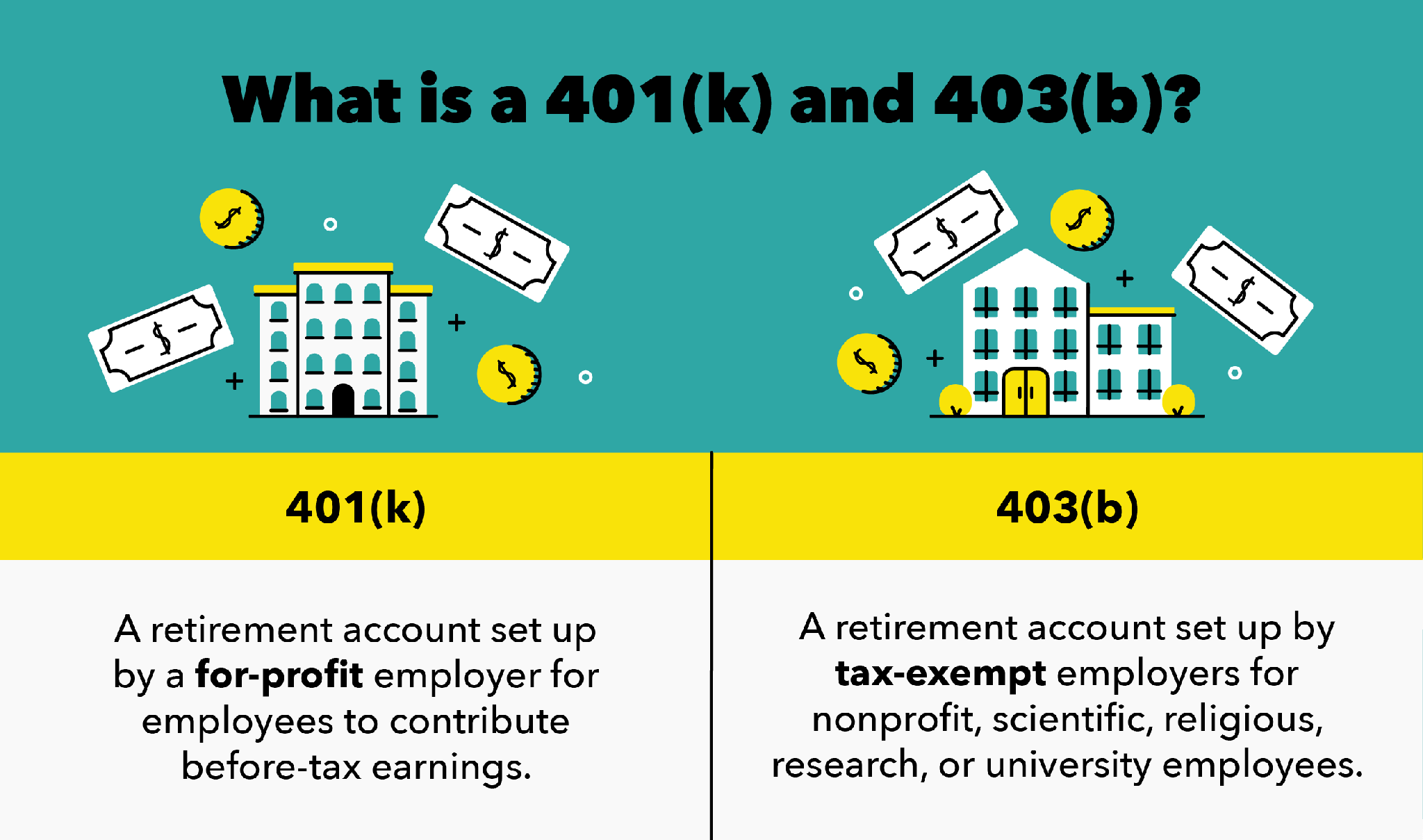
- Eligibility: 401 retirement plans are issued by for-profit employers and the self employed, 403 retirement plans are for tax-exempt, non-profit, scientific, religious, research, or university employees. As well as Hospitals and Charities.
- Investment options: 401s offer more investment opportunities than 403s. 401 accounts may include mutual funds, annuities, stocks, and bonds, while 403 accounts only offer annuities and mutual funds. Each employer varies in retirement benefits reach out to a trusted financial advisor if you have questions about your account.
- Employer expenses: 401 accounts are generally more expensive than 403 accounts. For-profit 401 accounts may pay sales charges, management fees, recordkeeping, and other additional expenses. 403 plans may have lower administrative costs to avoid adding a burden for non-profit establishments. These costs vary depending on the employer.
- Nondiscrimination testing: This form of testing ensures that 403 retirement plans are not offered in favor of highly compensated employees . However, 401 plans do not require this test.
Read Also: How To Use Your 401k
Plan Vs 403 Plan: An Overview
The public sector may be the last bastion of the defined-benefit planthat old-fashioned pension, calculated by the employer that came to employees automatically after they retired.
But nowadays, no single source of income may be enough to ensure a comfortable retirement. People also need to save on their own. Public-sector and nonprofit organizations don’t offer 401 plans that employees can contribute to. However, they can and do offer other employer-sponsored plans: the 403 and the 457.
How Much Should I Contribute To My 401
Most financial experts say you should contribute around 10%-15% of your monthly gross income to a retirement savings account, including but not limited to a 401.
There are limits on how much you can contribute to it that are outlined in detail below.
There are two methods of contributing funds to your 401.
The main way of adding new funds to your account is to contribute a portion of your own income directly.
This is usually done through automatic payroll withholding ).
The system mandates that the majority of direct financial contributions will come from your own pocket.
It is essential that, when making contributions, you consider the trajectory of the specific investments you are making to increase the likelihood of a positive return.
The second method comes from deposits that an employer matches.
Usually employers will match a deposit based on a set formula, such as 50 cents per dollar contributed by the employee.
However, employers are only able to contribute to a traditional 401, not a Roth 401 plan.
This is especially important to keep in mind if you want to utilize both types of plans.
A key variable to keep in mind is that there are set limits for how much you can add to a 401 in a single year.
For employees under 50 years of age, this amount is $19,500, as of 2020. For employees over 50 years of age, the amount is $25,000.
If you have a traditional 401, you can also elect to make non-deductible after-tax contributions.
Plan in Advance
You May Like: When Leaving A Company What To Do With 401k
What Are Your Options If You Leave Your Employer
If you leave your job, you have several options for what to do with your 401 or 403 account:
- Roll over your account into your new employers plan.
- Roll over your account into an Individual Retirement Account .
- Some companies will allow you to leave your balance in its plan .
- Withdraw your account balance in a lump sum cash payout. This option, however, isnt advisable because youll incur steep income taxes on top of a 10% early withdrawal penalty.
Suggested Next Steps For You
Both 401k and 403 plans are powerful savings vehicles, especially if the employer makes contributions. One is not necessarily better than the other, and most employees dont have a choice of which plan to use, so the most important thing to focus on is diligent, disciplined savings over time to pursue your long-term financial goals.
The content contained in this blog post is intended for general informational purposes only and is not meant to constitute legal, tax, accounting or investment advice. You should consult a qualified legal or tax professional regarding your specific situation. Keep in mind that investing involves risk. The value of your investment will fluctuate over time and you may gain or lose money.
Any reference to the advisory services refers to Personal Capital Advisors Corporation, a subsidiary of Personal Capital. Personal Capital Advisors Corporation is an investment adviser registered with the Securities and Exchange Commission . Registration does not imply a certain level of skill or training nor does it imply endorsement by the SEC.
Recommended Reading: Should I Convert My 401k To A Roth Ira
What Is 401k Plan
The 401k plan is a savings plan that enables you to put up a certain percentage from your income before you pay taxes.
This, in turn, reduces what your taxable income should be annually. Coined from a section of the IRS code, 401k became a law in 1978.
Currently, this plan has availed a good number of Americans to invest about $5.8 trillion. It is important to note that while your salary is deducted, it doesnt lie effortlessly in the plan.
It undergoes a cyclical motion of going to work and producing profits.
Vs 403 Vs 457 Plans: Compare Employer
401 vs. 403 vs. 457 the plan titles are used almost interchangeably when it comes to discussions of retirement.
But apart from the fact that all three are employer-sponsored plans, what do they have in common, and how are they different?
Surprisingly, the three popular employer-sponsored retirement plans have more in common than not.
The main differences are the employers who offer them, and maybe a few small details beyond that.
Whichever plan is offered by your employer, you should take full advantage and participate to the extent your finances will allow.
These are three of the most generous retirement plans available, offering a combination of:
- tax-deductible contributions,
- often, employer matching contributions.
Don’t Miss: How To Take Money Out Of 401k Without Penalty
A Final Word On 401a And 403b Retirement Plans
Knowing which plan you qualify for with your employer will help you be able to make the right decision about your contributions. Both plans are very similar in structure, with only a few exceptions separating the two.
Each plan allows you to save for retirement. Each gives you choices in how you can grow your wealth, with specific contribution caps in place that you must consider. Over time, and with the catch-up contributions allowed, you can use this tool to effectively save for the future years to come.
Are There 401 Contribution Limits
Yes, there are annual contribution limits mandated by the Internal Revenue Service. In 2017, your individual contributions may not exceed $18,000.
If you work for a company that offers matching contributions, the total annual contributions may not exceed the lesser of a) 100% of your total annual compensation or b) $54,000.
Read Also: How To Invest In A 401k For Dummies
What Are The Contribution Limits Of The 401a And 403b Retirement Plans
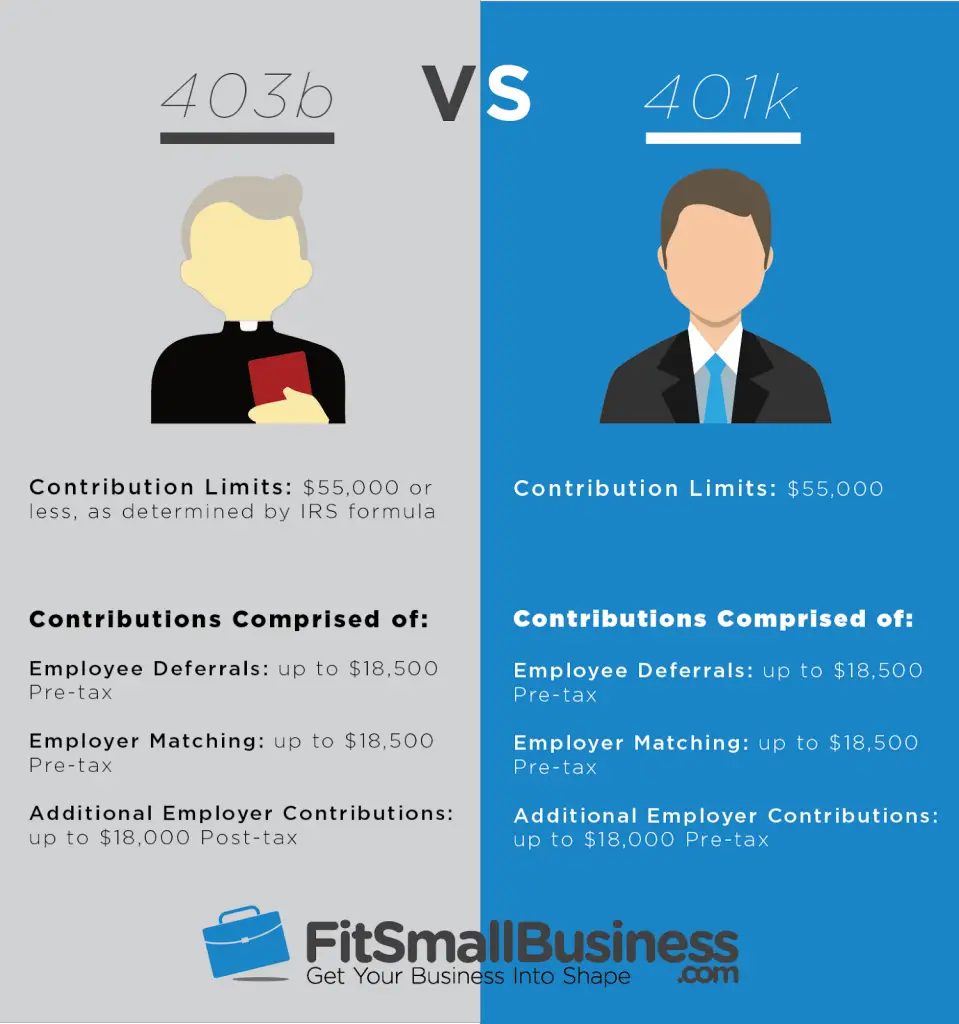
Unlike the 401k, which offers a normal limit of $18,500 in the 2018 tax year, the 401a plan permits contributions up to $55,000 per year to be made to the plan. For most people, however, there is a set contribution from the employee and the employer that goes into this plan.
According to IRS rules, it is not permitted to contribute more to the plan than what the employee earns in salary from the employer. That means a worker earning $34,000 per year is permitted a maximum $34,000 contribution to their 401a plan.
With a 403b plan, there is a limit to the number of elective deferrals permitted. Employees in 2018 are allowed to contribute $18,500 to their retirement plan during the calendar year. Employees who are above the age of 50 are also permitted to make a catch-up contribution of $6,000 beyond the basic limits.
There is also a limit on the annual additions permitted with a 403b retirement plan, which is the combination of all employer contributions and elective deferrals by the employee. This limit is the same as it is for the 401a plan, capped at $55,000 for the year in 2017. If you make less than that in salary, then your salary becomes the maximum contribution permitted with both combined.
Ways To Grow Your Retirement Savings
Contributing to a 401 or 403 can help grow your investments at a reduced risk. Youre able to grow your non-taxed income to put towards your future goals. The more you contribute, the more you may have by the time you retire. Here are a few tips to get ahead of the game and invest in your financial future.
Don’t Miss: How Do I Find Out Where My Old 401k Is
How Do 401 And 403 Plans Work
- Participation in a 401 or 403 plan is optional for employees.
- You decide the percentage of your salary that youd like to contribute, and that amount comes out of your paycheck and goes into your account every pay period.
- You decide how you invest your money. Your employers plan has a selection of investments for you to choose from. Most plans offer a diversified spread of mutual funds, including stocks, bonds and money market investments.
- When you leave your job, you still own your account your employer cant touch your funds.
The Difference Between A 403b And A 401k
Most companies today offer employees a standard 401 retirement deferred savings plan. However, if a person works for the government or some organizations, like nonprofits, different options can come up, including the 403 plan. This raises the question of which is better between a 401 vs. 403.
A variety of retirement plans exist today, approved by the Internal Revenue Service as legal tax shelters for earnings. In almost all cases, except for a Roth IRA, the plans involve pre-tax income that is deferred to a holding account and allowed to gain profit and interest through compounding and investment.
When the funds are finally withdrawn, usually later in a persons life, they should in theory be part of a larger retirement balance which can be used when a person is no longer working, ergo at a lower tax rate.
This maximizes the value of the dollars saved, even with inflation taken into account. Each of these plans has a numerical name, referring to the tax code statute that authorizes the activity and given plan.
You May Like: Can I Rollover 401k To Ira While Still Employed
Difference Between 401k And 403b
Categorized under Business,Finance,Investment | Difference Between 401k and 403b
401k and 403b are both retirement plans that can be adopted in a profit organization and non-profit organization respectively, and they are regulated by the internal revenue service with the internal revenue code of 1986.
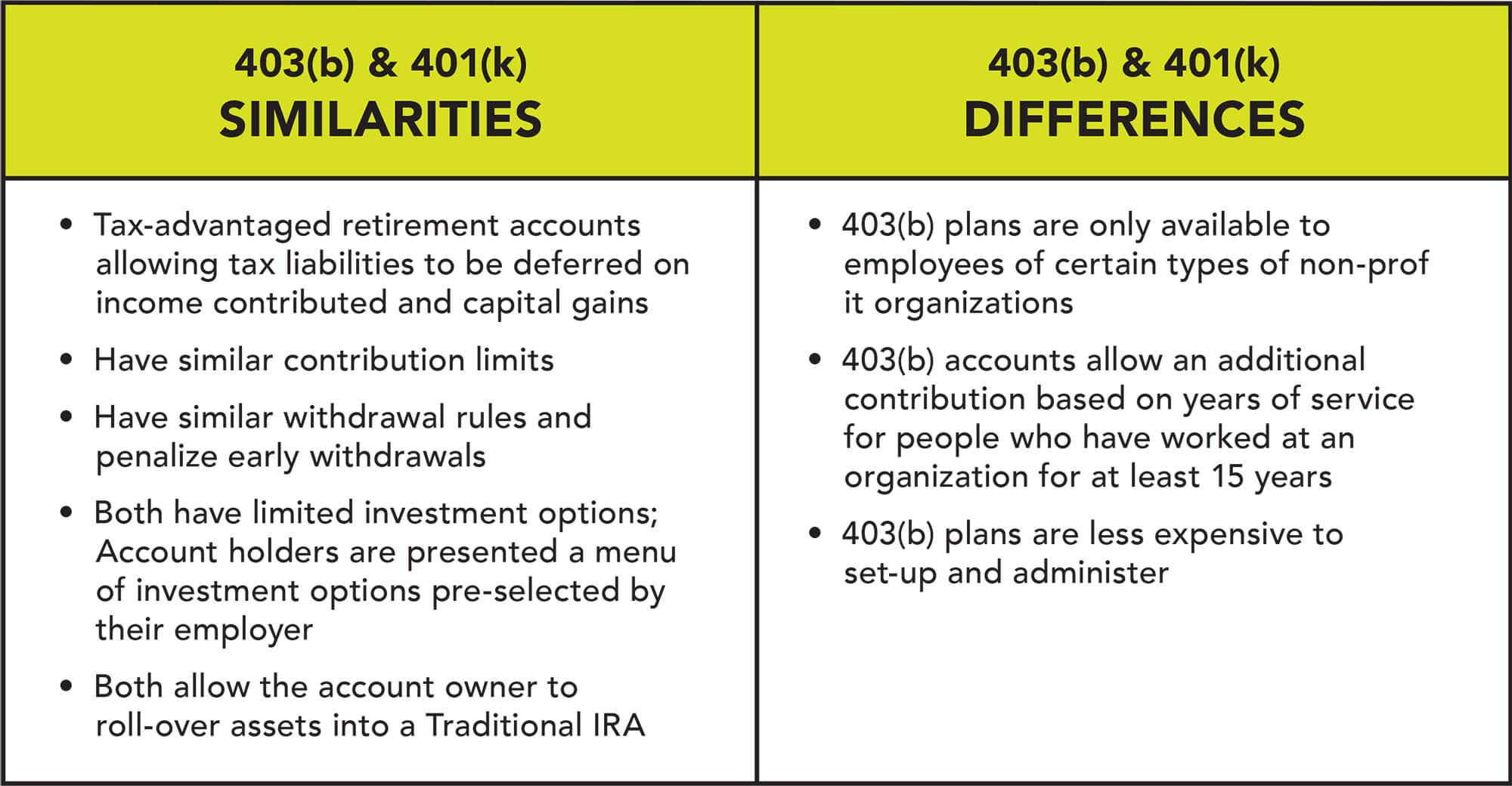
Though they do share some similarities, such as: limit on how much money that can be contributed, both plans encourage employer-employee contributions, and there is the possibility of withdrawing out savings before the age of 59 ½ though, terms and conditions are applied.
However, there are notable differences between both plans that make them differ in operation.
Differences Between 401 And 403 Plans
401 and 403 plans have a lot in common, but heres what sets them apart:
- Eligibility: 401 plans are offered by for-profit companies, and 403 plans are offered by tax-exempt organizations, such as hospitals, schools, universities, nonprofits and religious organizations.
- Investment Options: 403 plans only offer mutual funds and annuities, but 401 plans offer mutual funds, annuities, stocks and bonds. Because 401 plans are more expensive for the company, they usually offer a wider range and sometimes better quality of investment options.
- Employer Match: Both plans allow for employer matching, but fewer employers offer matches with their 403 plans. If an employer who offers a 403 does offer a match, they have to comply with regulations created by ERISAthe Employee Retirement Income Security Actwhich was passed in 1974.3 Most employers want to avoid these regulations because they cost time and money.
- Cost: 403 plans have lower administrative costs because the government doesnt want to place extra burdens on nonprofit organizations. 401 plans are more expensive for employers. But dont worrythis doesnt really affect you as the employee.
You May Like: Can I Sign Up For 401k Anytime
