Reading And Understanding The Summary Annual Report
The first thing you should do is discover exactly what is going on. You should have statements and contracts relating to the agreements you signed, as well as prior-year tax returns. To figure out where your money is going, use a computer program or a pen and paper.
As of 2009, the amount of information on your 401 report summary will be greater, including a more detailed account of the costs you pay to maintain it. Inquire about any line items that are unclear and double-check with your own research.
Request for Updated Materials
You may occasionally wait months for your fund reports to arrive. Even if you are charged an additional fee to receive a new statement, you are entitled to one. To make an informed decision about whether your fund sub-components are suitable candidates for weathering a bear market, you will need up-to-date information on your funds performance and diversification.
Investment funds can change rapidly, especially in a volatile market. Be sure your reports include historical data and some sort of standard to compare performance against that makes sense. This will help you understand how the fund is performing over time and make more informed decisions about investing.
Historical Performance Analysis
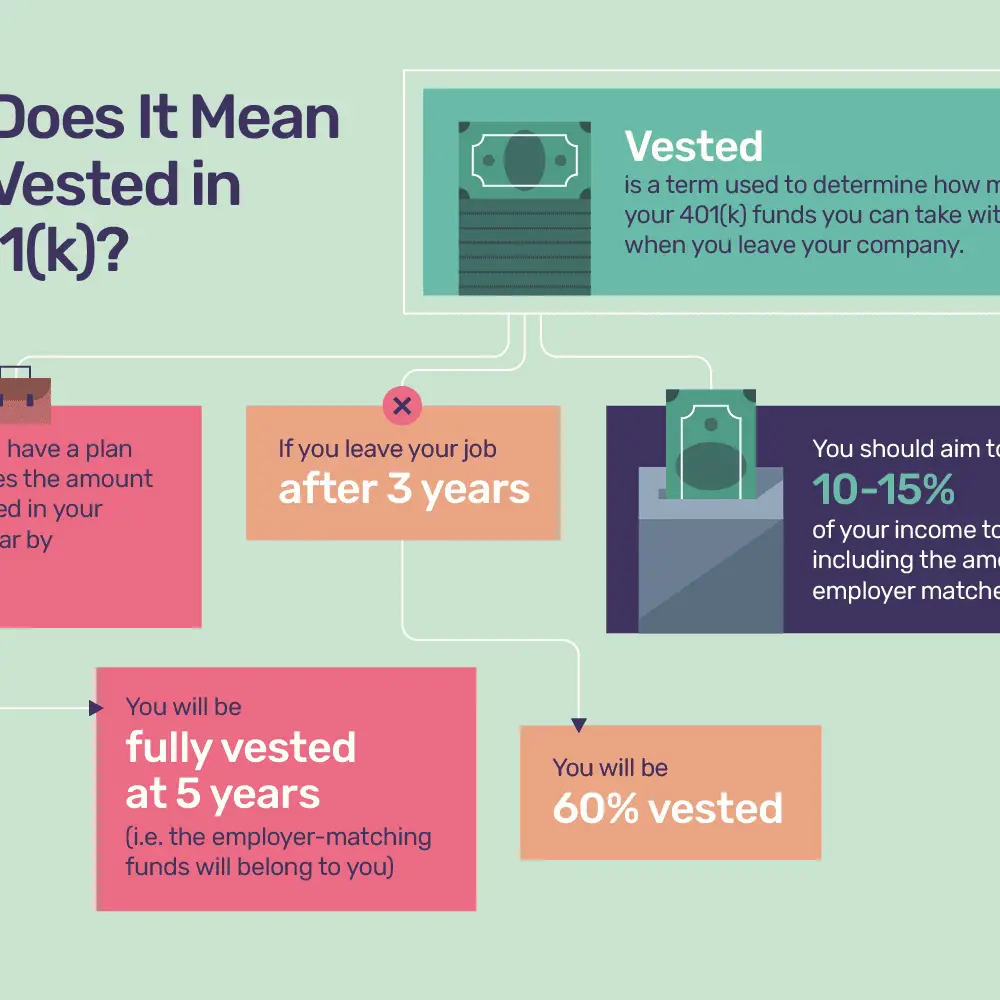
Employees Contribution Vs Employers Contribution
The employeeâs contributions to a 401 plan are 100% vested, and the money belongs to them if they leave the company. If youâve only made a single contribution to the 401 when you decide to leave, you can choose to rollover to IRA or cash out as a lump sum. However, if you decide to cash out early, you will need to pay taxes and early withdrawal penalties.
In contrast, you don’t own the employer’s match right away, unless your employer offers immediate vesting. Immediate vesting occurs when the employer uses a safe harbor match, which allows the employee to be 100% vested in the employer’s contributions to a 401. However, the regular employer’s match is subject to a vesting schedule, and you will have to wait for the required vesting period to get full access to the employer’s match.
What Happens If A Participant Terminates Who Is Not Fully Vested
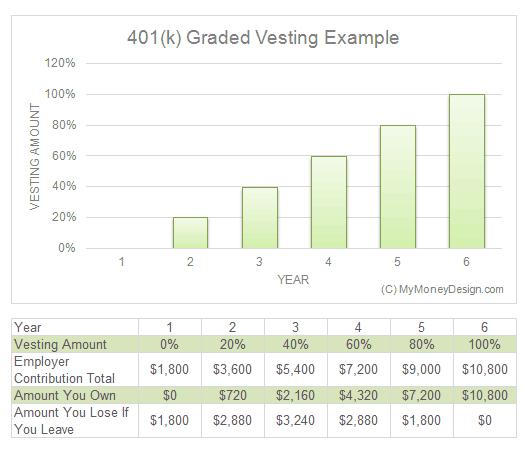
Basically, the employee forfeits the non-vested portion of their account.
For example, if an employee has $1,000 in their account and is only 60% vested at the time employment is terminated, receive only $600. The remaining $400 is forfeited.
If allowed in the plan document, forfeitures typically can be used to cover plan expenses, fund future employer contributions, or increase the accounts of the remaining plan participants.
Recommended Reading: Can I Convert My 401k To A Roth
What Is Immediate Vesting
In 2015, about 40 percent of companies allowed matching contributions to vest immediately. In this case, the employee owns 100% of their account balance, which includes their contributions and the contributions matched by the employers. If your company allows immediate vesting, you can leave your job today and still own 100% of the contributions you made yesterday and those matched by your employer.
In yet another situation, the employee can allow you to vest 100% of the contributions they match if the company utilizes a safe harbor match. However, if your employer does not permit immediate vesting, it is because their vesting schedules do not allow it.
What Happens When Youre Fully Vested
Once youre fully vested, the full value of your employers contributions are yours and typically all future employer matches vest immediately. These will continue to be invested according to your plan and will be available to you in the event you leave the company. At that time, youll have the option of rolling over the account into the plan offered by your new employer, or into an IRA, which gives you greater investment options.
Here are some additional details about vesting that are useful to know:
- Vesting often takes place over a few years, typically three or four years.
- An employer match often vests proportionally each year, and this process is called graded vesting. For example, if your match vests over four years, one-fourth of the total matching amount will vest each year.
- Another type of vesting cliff vesting takes place all at once. Once you surpass the vesting period, 100 percent of your match belongs to you.
Why would a company require a vesting period? A vesting period may reduce employee turnover and keep employees on the job longer, helping reduce the employers costs. Other benefits such as stock or option plans for employees may also have a vesting period.
While its normal for 401 plans and others to require a vesting period, other retirement plans such as the and SIMPLE IRA require immediate vesting.
You May Like: How To Find Out If I Have 401k
What Does 401k Vesting Mean
When your employer makes matching contributions to your 401k, they will often delay the transfer of ownership to you. Any funds you contribute yourself belong to you right away, but the company match amounts are typically transferred to you gradually over one or more years. This transfer of ownership is what is meant by the term vesting.
Once an employer match has fully vested, you have total ownership of those funds. You own them outright and they are yours to keep if you decide to leave your employer, are laid off, or even get fired.
What Happens When You Dont Have Full 401 Vesting
If you dont have full 401 vesting, it follows that you will not own the entire amount in your retirement plan. You will only be entitled to the amount you contributed directly, and your employers matched contributions that are vested.
There are two crucial points that you should always remember about vesting. The first is that the money was never yours to begin with. When you terminate your employment and fail to get the matched contributions that werent vested, you have lost nothing. However, staying for an extra one or two years to benefit from full vesting is usually worth it.
The second point touches on the employer. The contribution matches are an added advantage to the worker. The company is acutely aware that offering a favorable contribution match to the employee is a strong hiring incentive. But because they intend to reduce the chances of workers leaving their jobs, they must apply vesting schedules to ensure that they stay around for a little bit longer.
The plan benefits both parties. For the employee, the match contributions offer a retirement cushion that they can immediately own after it is fully vested. To the employer, it ensures that the workers stay in their jobs for at least a couple of years.
Read Also: How To Get Money Out Of My 401k
What Is A Qualified Retirement Plan
A qualified plan is simply one that is described in Section 401 of the Tax Code. The most common types of qualified plans are profit sharing plans plans), defined benefit plans, and money purchase pension plans. In general, your contributions are not taxed until you withdraw money from the plan. Most retirement plans that you obtain through your job are qualified plans.
Can I Withdraw That Money
Access to funds in your retirement account depends on your situation.
After You Leave Your Job
Once you quit, retire, or get fired, you should have access to your vested balance. You can withdraw those funds and reinvest in a retirement accountor cash out, although there may be tax consequences and other reasons to avoid doing so.
While Still Employed
While youre still employed, you typically have limited access to money in a retirement planeven your fully vested balance. Rules may require that you meet specific criteria and that your plan allows you to access your money. There are several potential ways to withdraw money before you leave your employer:
Other Situations
You might become fully vested in all of your balances if your employer terminates or shuts down the retirement plan, enabling you to transfer the funds elsewhere. Likewise, death or disability can trigger 100% vesting. Check with your employers plan administrator to learn about all of the plans rules.
Don’t Miss: How Much Can You Transfer From 401k To Roth Ira
Whats A Good Employer Match And Vesting Percentage
A common annual employer match is 100% of the employee contribution up to 3% of one’s salary. This means that if you contribute $50 in each paycheck, the employer will match that $50 up to 3% of the paycheck amount. That means that if an employee makes $2,000 per paycheck, the employer will match up to $60 per paycheck. Contributing only $50 doesnât max out the free money an employee can get from the employer.
When You Can Collect Private Pension Plan Benefits
Being fully vested in your pension does not mean that you can access the money immediately. Under federal law, employees earn the right to receive their pension benefits when they reach normal retirement age, in addition to meeting the years of service requirements described above.
Normal retirement age for an ERISA-covered plan is defined by the plan, Lowell says. However, it may not occur later than age 65 with five years of service.
Also Check: Who Can Open An Individual 401k
The History Of 401 Plans
The tax code changed in 1978, unintentionally prompting the creation of the 401 savings plan that has largely supplanted company-funded pensions. Intended to clarify the legal status of some extremely wealthy investors existing saving plans, this minor rule adjustment sparked a decade-long financial industry and market boom in the 1990s.
Since the 1980s, when the 401 plan was established in a single financial institution, these plans have evolved into a government-sponsored private investment intended to help employees save for retirement in order to augment their Social Security income. In the first six years of the program, several hundred thousand businesses provided plans as an incentive to their staff. These savings accounts were offered as an option benefit to individuals of all sorts of professions throughout the 1990s.
In 1988, following a series of legislative actions designed to boost participation rates in 401 plans among US workers, the Congress passed a legislation that made employee contributions the default option for all firms offering such programs. Employees wanting to opt out of making 401 contributions have been required to fill out a form stating their wish to do so.
Reasons for Supplemental Retirement Savings
Social Security benefits, in combination with Medicare and Medicaid, are generally not considered adequate alone for sustaining one above the poverty level in retirement.
Inadequacy of Social Security Coverage
Medicare and Medicaid
IRA Plans
Can You Withdraw From 401k
What is a 401 and IRA penalty withdrawal? Generally, if you withdraw money from a 401 before the plans normal retirement age or from an IRA before turning 59 ½, youll pay an additional 10 percent in income tax as a penalty. But there are some exceptions that allow for penalty-free withdrawals.18 nov. 2021
Don’t Miss: Is Fidelity Good For 401k
How Does 401k Vesting Work
When you participate in a 401k plan, you and your employer contribute a prearranged sum of money to your account each pay period. The money you contribute to your 401k is always 100 percent yours but you must be fully vested to claim all of the money your employer contributes. Vesting typically takes three to six years depending on your companys plan.
Fully vested, by definition, means that you own all the funds in your account. During the time period that it takes to become fully vested, you can be partially vested. Being partially vested means that you dont own all of the funds your employer has contributed but you might own a certain portion depending on how long youve worked for your employer.
Learn: Borrowing From Your 401k What You Need to Know
Reinvesting In Stable Funds
The word stable is subjective when the market is constantly changing. We can make assumptions about what will remain stable during a recession by observing past performance or current trends.
Many investors consider bonds to be a very safe haven during economic downturns. This does not include certificates of deposits or the enormous amount of commercial paper that many individuals have become acquainted with for the first time in 2008.
In contrast to stocks, the other type of security, bondholders lend money rather than invest it. As a result, bankruptcy laws favor lenders rather than part-owners . In the event of bankruptcy, you will be able to liquidate your assets before other creditors.
Although some experts believed that dividends in the most stable firms might be secure for 401 investments because of natural economic growth, the severity of the current financial crisis has made this market significantly riskier than it has been in a long time, with few firms capable of generating dividend profits to share in either stock offerings or cash payments.
One needs to be sure they do not trade stability for actually falling behind the rate of inflation, which is a losing proposition as far as the relative value of that money. In early 2008, when the inflation rate was around 3%, many 401 funds had returns at the same rate. After administrative costs and other fees, many people were losing money on their plans but were unaware because they had not liquidated them yet.
Don’t Miss: How To Cash Out On 401k
How Does Vesting Affect How Much I Should Contribute To Retirement
You should aim to contribute 10 to 15 percent of your income to retirement. This total can include your employer match. If this amount is a bit out of your reach, then you should aim to contribute at least the same amount your employer matches. After all, it’s basically free money.
And if you know you are going to leave a particular job before your 401 is fully vested, you may want to increase your contributions to cover the loss if you change jobs.
To Seek Venture Capital
A vesting schedule is also essential for businesses seeking venture capital.
Michele Schueli, general partner and venture capitalist with a global portfolio of early and late-stage companies at Armyn Capital, says early-stage financial backers of companies often encourage the use of vesting schedules for stock options, usually four years with a one-year cliff for employees, or longer for company founders.
“Disregarding vesting is a problem for investors as it leads to a capitalization table filled with ‘dead equity,’ which is equity owned by founders/employees who left the company and are not adding any value,” Schueli, says. “Ultimately, ‘dead equity’ blocks result in a chaotic capitalization table, which makes it difficult for investors to fund the company, even if all other boxes have been ticked.”
Recommended Reading: When Leaving A Company What To Do With 401k
Types Of Money That Might Vest
Examples of money types that are most likely to have a vesting schedule include:
- Employer matching: Any funds you receive as a result of your own contributions to the plan.
- Employer profit-sharing: Money you might get regardless of whether or not you contribute.
- Others, potentially
Examples of contributions that would generally not require any wait for vesting:
- Qualified non-elective contribution : An employer contribution thats typically used to fix mistakes or solve failed discrimination tests. For the contribution to work, it must be 100% immediately vested.
- Qualified matching contribution : Similar to a QNEC, above, but handled differently.
- Rollover: Funds that you roll into your plan from a previous employers 401, 403, your IRA, etc.
IRA-based accounts, including SEPs and SIMPLEs, do not have vesting schedules. Once the money goes into your account, its yours to do with as you please. However, its critical to learn about potential tax consequences of moving or withdrawing funds from any retirement account.
Important: Speak with your tax advisor and your plan administrator before making any decisions. The information here might not apply to your plan, it may be outdated, or there may be errors or omissions that you need to address with a professional.
Next Up: Curious About Meeting?
What Does Fully Vested Mean
Fully vested means a professional has full rights to a benefit account. Some people may use this term to describe stock options or profit-sharing, but this term most often applies to employer 401k plans. Many companies offer 401k plans as a benefit for employees. With a 401k plan, employees can invest part of their paychecks into a retirement savings fund. The amount that comes from an employee does not need time to vest. The employee automatically has rights to this money. Vesting only applies to funds contributed by an employer.
Some employers offer 401k match programs, which may follow a vesting policy. With 401k match programs, companies offer to match employee contributions up to a certain percentage. For example, if an employee contributes 3% of their paycheck to their 401k plan, an employer would match this amount and make an additional 3% contribution. These funds often need to vest before the employee has rights to them.
Vesting is the time it takes before an employee can access all of their 401k funds, including the employer contributions. Each company sets its own vesting schedules and plans, but typically this process takes three to seven years. Once fully vested, an employee owns all the money in their 401k, even if they leave the job or decide to open an individual retirement account.
Read more:How Does a 401 Plan Work?
Don’t Miss: When Can I Take Out 401k
What Is A 401
A 401 is a type of retirement account known as a defined contribution plan. The employee contributes funds to the retirement account. These contributions are deducted from the employee’s paycheck and can be made with either before- or after-tax dollars, depending upon the choices permitted within the plan. Contributions made to a plan are held in a 401 account. An employer may also make contributions to the employee’s 401 plan.