You Can Only Contribute Income That Is Reported On Your W
- Income and dividends not reported on your W-2, including those reported on your K-1, are not eligible for contribution. This may require extra planning on your part, taking into consideration your self-employment tax liabilities and planned annual plan contributions.
- However, even with a low W-2 salary through the S-corporation, you will still be able to conduct superior annual contributions to the 401 .
Can My Llc Have A 401k
The federal tax law allows employees to participate in an employers 401k plan to take advantage of tax deferrals to contribute to retirement accounts. However, if you are an independent business member of a small business that operates as an LLC, the IRS allows you to set up a 401k plan for yourself.
Can single member LLC contribute to 401k?
If your LLC is a single-member entity, your maximum revenue share contribution can be up to 20% of your net compensation . The total contribution to your Solo 401k plan is the aggregate of your salary deferral and profit-sharing contribution.
Can an LLC have a 401k plan?
Can LLC owners contribute to a 401 ? Solo 401 plans are not limited to single proprietorships. Businesses that are structured as limited liability corporations , as well as partnerships, can also participate in these plans if they meet all of the requirements.
The Most Common Types Of Plans
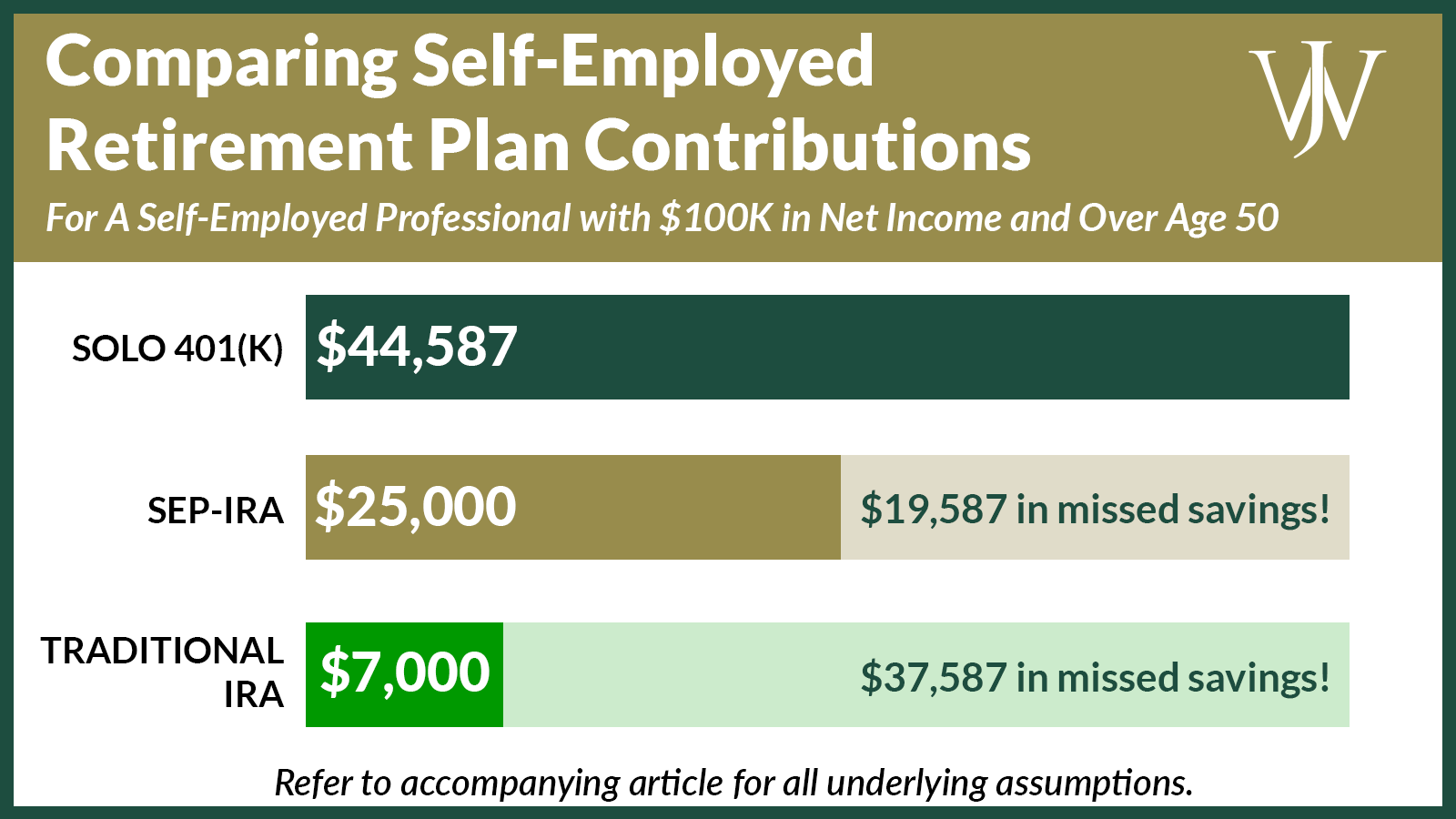
Simplified employee pensions, commonly knows as SEPs or SEP-IRAs, are simple and flexible. They allow you to contribute up to 25% of your business income, with a cap of $54,000 for the 2017 plan year. The plan will not lock you into a contribution amount, so you can always contribute less than the maximum — or nothing at all.
If you’ve waited until the last minute to figure out your retirement plan options, this may be the plan for you: You can open a SEP as late as the extended due date of your income tax return.
Solo 401s. If the contribution limits on a SEP aren’t quite high enough for you, a solo 401 might be what you are looking for. This 401 plan for self-employed individuals allows you to contribute up to $18,000 plus 20% of your business income . If you are older than 50, the deferral limit is $24,000 for 2017 and the cap is $60,000. As with a SEP, you have the option of contributing little or no money in leaner years.
This type of plan requires more paperwork than a SEP IRA. When your account grows to $250,000 or more, you will have to file a special tax return for the plan. In addition, a solo 401 costs more than a SEP to establish and maintain.
You must establish the plan by December 31 of the year in which you want to make the contribution .
Also Check: Can I Use My 401k To Buy Investment Property
Calculations For A S Or C Corporation Or A Llc Taxed As A Corporation
S corporations, C corporations and LLCs electing to be taxed as a corporation pay the business owner a W-2 salary. The calculation of how much can be contributed to a Self Employed 401k is based only on the W-2 salary of the self employed business owner .
Salary Deferral Contribution:
In 2020, 100% of W-2 earnings up to the maximum of $19,500 or $26,000 if age 50 or older can be contributed to a Self Employed 401k .
Profit Sharing Contribution:
A profit sharing contribution up to 25% of W-2 earnings can be contributed into a Self Employed 401k.
- EXAMPLE 1A 50 year old self employed consultant is the owner of a Subchapter S business with $50,000 of W-2 earnings in 2020. In this example, the consultant could contribute $26,000 of salary deferrals + $12,500 profit sharing contribution = $38,500 Total Self Employed 401k contribution.
- EXAMPLE 2 A 50 year old self employed consultant is the owner of a Subchapter S business with $100,000 of W-2 earnings in 2020. In this example, the consultant could contribute $26,000 of salary deferrals + $25,000 profit sharing contribution = $51,000 Total Self Employed 401k contribution.
How To Open Your Solo 401
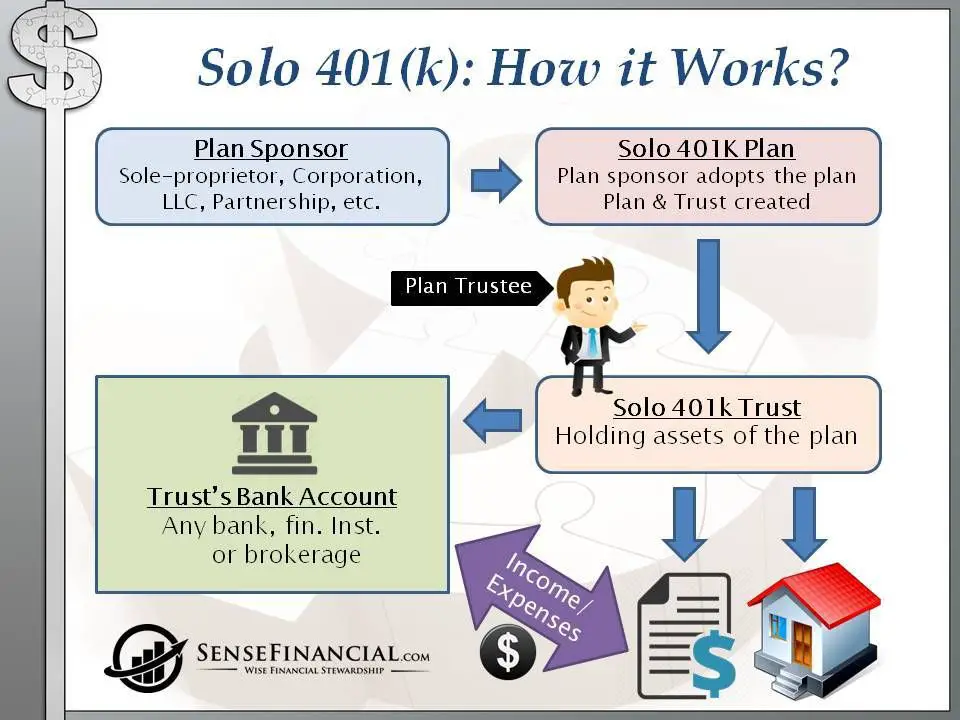
Opening your account is fairly straightforward. You can open this type of account at most online brokerage firms or with your local financial planner if you prefer. You must have your Employer Identification Number handy, and you will be required to put the details of your plan in writing. This means that you will have to write down the type of account you will be opening as well as the types of investments that will be included in the plan. This could include mutual funds, stocks, bonds, ETFs, or other investment avenues. You will also be required to use the IRS Form 5500-EZ to report the returns from your plan each year before the tax filing deadline.
You May Like: How Can I Withdraw My 401k
Big Advantages Of A Solo 401k
1. Pro: Running your own business is rewarding.
2. Pro and Con: You need to run your own business and make adequate money to fund your life and the Solo 401k investment.
3. Pro: Massive contribution limits enable you to make up any lost time pretty quickly. This is great if you didnt save as early or as much as you would have liked.
4. Pro: Many tax benefits supersized.
5. Pro: You can make up lost time pretty quickly for what was missed in the early years, assuming you dont actually need too much of the earnings from the self-employment to get by.
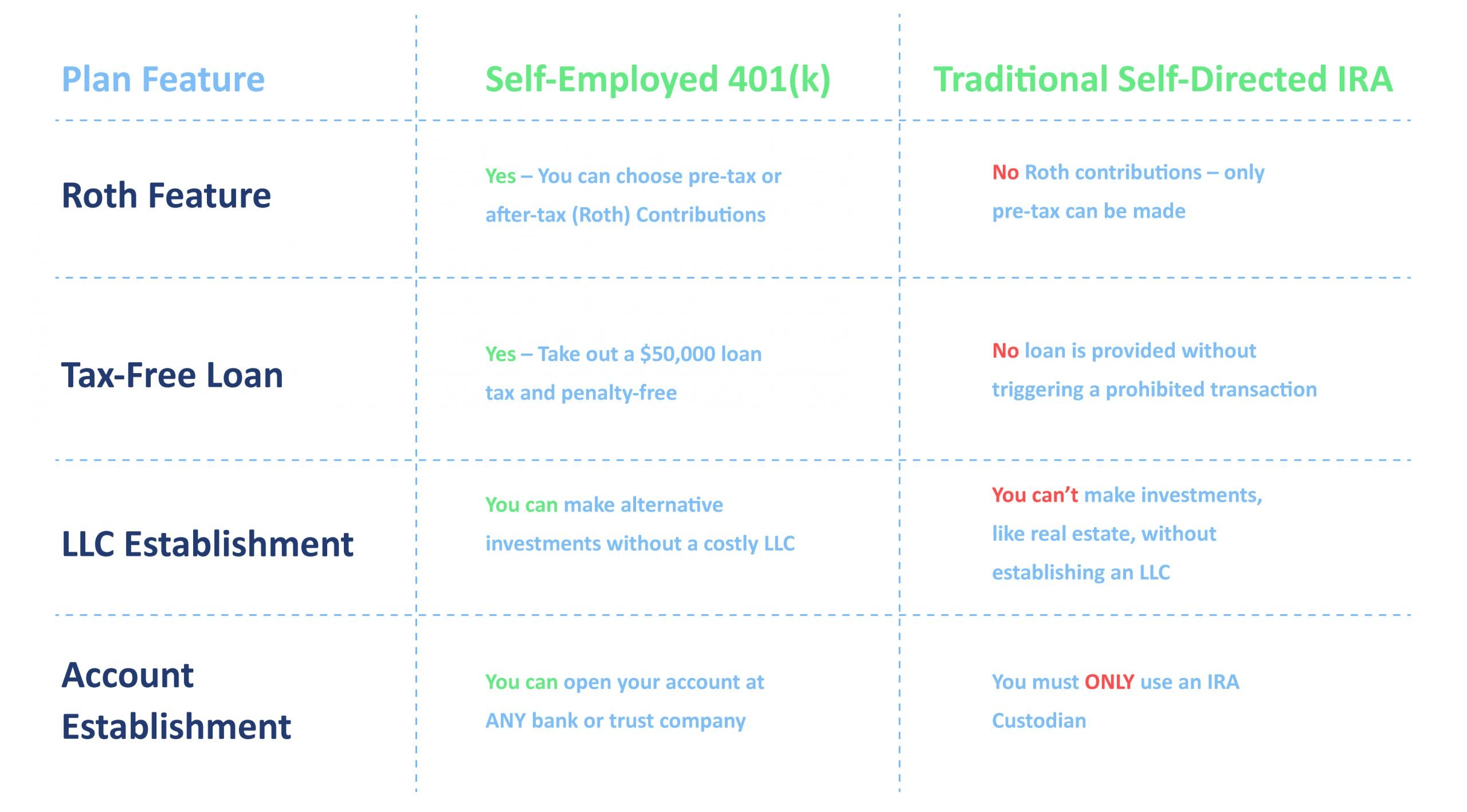
6. Pro: Roth options are possible. This is massively compelling to people who wanted to save in a Roth account because they think that tax rates will be higher in the future, but could not due to high earnings.
NOTE: You can only contribute to a Roth plan with your employee contributions, not employer.
7. Pro: Relatively simple to set up.
8. Pro: Flexible investment options.
9. Pro: With a Solo 401k you can borrow up to $50,000 or 50% of your account value whichever is less at a low interest rate. The loan can be used for any purpose.
10. Pro: You control the account. You do not need a custodian to administer the account.
11. Pro: The plans are easy to operate and dont generally have any hidden fees.
Next Steps To Consider
Keep in mind that investing involves risk. The value of your investment will fluctuate over time, and you may gain or lose money.
The change in the RMD age requirement from 70½ to 72 only applies to individuals who turn 70½ on or after January 1, 2020. Please speak with your tax advisor regarding the impact of this change on future RMDs.
Fidelity does not provide legal or tax advice. The information herein is general and educational in nature and should not be considered legal or tax advice. Tax laws and regulations are complex and subject to change, which can materially impact investment results. Fidelity cannot guarantee that the information herein is accurate, complete, or timely. Fidelity makes no warranties with regard to such information or results obtained by its use, and disclaims any liability arising out of your use of, or any tax position taken in reliance on, such information. Consult an attorney or tax professional regarding your specific situation.
This information is intended to be educational and is not tailored to the investment needs of any specific investor.
Don’t Miss: How To Add Money To 401k
Should I Choose A Traditional Or Roth Solo 401
For many investors, deciding between a traditional or Roth solo 401 comes down to whether you believe youre in a lower tax bracket today than you will be in retirement. If you think you are paying lower taxes now, you might choose a Roth solo 401. If you anticipate being in a lower tax bracket in retirement, a traditional solo 401 may be a better bet.
Theres another wrinkle with a Roth solo 401 account: You can only contribute up to $19,500 in 2021 , plus catch-up contributions of $6,500 if youre 50 or older. If youre able to save more than this amount, you will need to contribute the extra into a traditional solo 401 account. You can make both employer and employee contributions to a solo 401, but your employer contributions cannot be saved in a Roth account.
Flexibility To Choose Between Traditional & Roth
With an employer-sponsored plan, you are almost always stuck with a traditional plan. Many employers do not offer Roth plans because they are difficult to manage and maintain. A traditional 401 might not be the best option for you, and with a solo plan, you can choose which type of account you open. You might end up saving yourself thousands of dollars in tax benefits by having the flexibility to choose which type of account you open.
Read Also: How To Create A 401k
No Employees In Other Businesses
If you have a business that fits the qualification guidelines for Solo 401, you may not be eligible, however, if you or certain family members have ownership in other businesses that do have employees. The IRS defines a Controlled or Affiliated Service Group. If the same 5 or fewer owners have either 80% ownership or more than 50% effective control of one or more businesses, then those businesses are looked at as being one for purposes of plan qualification. If any business within such a group has employees, then all businesses within the group are treated as if they have employees.
You May Like: How To Calculate Employer 401k Match
Contribution Limits For Self
You must make a special computation to figure the maximum amount of elective deferrals and nonelective contributions you can make for yourself. When figuring the contribution, compensation is your earned income, which is defined as net earnings from self-employment after deducting both:
- one-half of your self-employment tax, and
- contributions for yourself.
Use the rate table or worksheets in Chapter 5 of IRS Publication 560, Retirement Plans for Small Business, for figuring your allowable contribution rate and tax deduction for your 401 plan contributions. See also Calculating Your Own Retirement Plan Contribution.
Also Check: How To Rollover A 401k Without Penalty
Use The Plan To Take Out A Loan
A great advantage of the Solo 401 is that you can use it to take out a loan tax and penalty-free. Under Internal Revenue Code Section 72, a Solo 401k Plan participant can borrow up to 50% of the total 401 value or $50,000 . Participants can borrow this for any purpose, such as paying off debt or funding your business.
Repayment of the loan is based on a schedule provided when the loan is initiated. You must pay the loan back over a term of up to five years. Participants must make loan payments at least quarterly and at a minimum interest rate of Prime. As of 03/28/22, the Prime interest rate as per the Wall Street Journal is 3.50%.
Failure to make the loan payments may cause a loan default causing taxes and IRS penalties.
What Are The Benefits Of A Solo 401
Unlike other options, a Solo 401 account holder can choose between a traditional option and a Roth option. The traditional option allows you to deduct the amount you pay in from your income for that year, giving you an immediate tax break. With the Roth option, the income taxes on that money is paid immediately and you owe no taxes when you withdraw the funds.
The Solo 401 has far higher annual contribution limits than a plain-vanilla IRA, although that is also true for the SEP IRA and the Keogh plan.
The Solo 401 allows you to take loans from your account before you retire. This is not an option with many other retirement plans.
Finally, the Solo 401 is relatively straightforward in terms of paperwork, as it is designed for one-person shops, not corporations.
Also Check: Should I Transfer 401k To New Employer
Solo 401 Establishment Deadline:
For 2021, in order to make employee contributions for 2021, the self-employed business owner had to establish the solo 401k plan by December 31, 2021. However, if the plan was established on January 1, 2022 or after by your business tax return due date including the business tax return extension, then you cam make employer profit sharing contributions for 2021 but cannot make employee contributions. For example, an employer operating the plan on a calendar-year basis had to complete the solo 401k plan documentation no later than .
For makin 2021 solo 401k plan contributions, the solo 401k has to be adopted by December 31, 2021 for self-employed businesses operating the plan on a calendar-year basis in order to preserve the right to make both employee and employer contributions in 2022 for 2021 by the business tax return including business tax return extensions. Otherwise, if the solo 401k plan is adopted on January 1, 2022 or after but by your business tax return due date including extensions, you will only be allowed to make employer contributions not employee contributions to the solo 401k plan. To learn more about the December 31, 2021 plan adoption/establishment deadline VISIT HERE.
Read Also: How To Start My 401k
How Do You Start One Of These 401 Plans
Bergman says you first need to select a provider. One of the most common ways to establish one of these plans is to go through a bank. You usually arent charged a fee for these, but your investment options are limited to the financial products the bank or financial institution sells. You can also go through a brokerage. In addition, there are self-directed solo 401 plan document providers, which do not sell investments and will allow you to establish a self-directed solo 401 plan to make alternative asset investments, such as real estate, as well as gain access to all other available plan options, such as Roth contributions and a $50,000 loan option.
Also Check: Where Can I Rollover My 401k To An Ira
Solo 401 Employee Contribution Limits And Rules
As an employee, you can contribute up to $19,500 a year. If youre 50 or older in 2021, you can contribute an additional $6,500 in what are called catch-up contributions.
Those amounts are total across all 401 plans. For example, if you run your own business and youre a W-2 employee at another company, you dont get to contribute $39,000. Your 401 employee contribution limit is still $19,500 total.
If your solo 401 plan rules allow, you can decide to make employee contributions to a Roth or a traditional solo 401.
If you have a spouse, he or she can contribute only up to the amount they earn from the business.
Employee contributions are due by Dec. 31 each year.
Solo 401 Vs Sep Ira Contribution Example
Consider John Smith who, in addition to his regular corporate salary, earns $150,000 of consulting income. The consulting income is earned and paid to his business, John Smith LLC, which files as a sole proprietorship. John wants to save more dollars from this consulting income in a tax-advantaged way. The below compares the total contribution possible with an SEP IRA vs. a Solo 401 plan:
Also Check: How Long To Transfer 401k To Ira
What Is A Self
This plan goes by many names, including solo, individual and single-k, but they all refer to a 401 retirement savings plan for a self-employed person. You can contribute a large amount of money to this plan every year and then start taking distributions from the account after you turn 59.5 years of age.
Key takeaway: A self-employed 401 plan is a retirement savings plan started and contributed to by a self-employed person.
If I Offer A 401 To My Employees Are There Compliance Regulations I Must Follow Or Can The Retirement Plan Provider Help With These
Certain employers who offer 401 and other retirement plans must abide by the Employee Retirement Income Security Act of 1974, as amended, which helps ensure that plans are operated correctly and participants rights are protected. In addition, a 401 plan must pass non-discrimination tests to prevent the plan from disproportionately favoring highly compensated employees over others. The plan fiduciary is usually responsible for helping comply with these measures.
This information is intended to be used as a starting point in analyzing employer-sponsored 401 plans and is not a comprehensive resource of all requirements. It offers practical information concerning the subject matter and is provided with the understanding that ADP is not rendering legal or tax advice or other professional services. For specific details about any 401 they may be considering, employers should consult a financial advisor or tax consultant.
Unless otherwise agreed in writing with a client, ADP, Inc. and its affiliates do not endorse or recommend specific investment companies or products, financial advisors or service providers engage or compensate any financial advisor or firm for the provision of advice offer financial, investment, tax or legal advice or management services or serve in a fiduciary capacity with respect to retirement plans. All ADP companies identified are affiliated companies.
You May Like: Can I Start A 401k
What Is A Solo 401
Just because you are a one-person outfit, a freelancer, or an independent contractor doesn’t mean you have to do without a retirement savings plan or the tax benefits that accompany them.
One option If you are self-employed is the solo 401, also known as an independent 401 plan. In fact, the Solo 401 has some benefits over other types of retirement accounts available to the self-employed.
How Much Does It Cost To Set Up A 401k Plan For A Small Business
Initial set up fees run $500 to $3,000, depending on the size of your company and the benefits you select. Simple 401Ks are less expensive. Expect to pay about $500 to $1,000 per year, plus $20 to $50 for each plan participant. Administrative services are billed at an hourly rate, generally $100 to $300.
Complex fee structures, as well as the assortment of plans available, make it difficult to identify specific costs for every 401 on the market. Costs of managing a plan are handled in a variety of ways. As described by the Department of Labor , plan fees are generally divided into four categories:
1.) Asset-based: expenses based on the amount of assets in the plan, represented as percentages or basis points. This also usually lumps in custodial fees. Typically 2-3%.
2.) Per-person: expenses based upon the number of eligible employees or actual participants in the plan. Can range from $8 to $750+ per month per person
3.) Transaction-based: expenses based on the execution of a particular plan service or transaction.
4.) Flat rate: fixed charge that does not vary, regardless of plan size.
You May Like: What Investments Should I Have In My 401k
