What Is A Roth Ira Conversion
Converting to a Roth IRA involves moving assets from your traditional IRA or employer-based retirement plan to a Roth IRA. While you’ll pay taxes on the pre-tax retirement assets in the year you convert, future earnings on your money will be tax-free in a Roth IRA and withdrawals will be tax-free as well, when you have met certain requirements.
How Do I Rollover If I Receive The Check
If you receive a distribution check from your 401 rollover to a Roth IRA, then chances are good they will hold around 20% for taxes. If you want a direct 401 rollover to a Roth IRA, you may want to send that check back to your employer 401 provider and ask to be sent all of your eligible retirement distribution directly to your new Rollover IRA account .
You have 60 days upon receiving the check to get the money into the Roth IRA- no exceptions! So dont procrastinate on this one.
What Are The Benefits Of A Roth Individual Retirement Account
A major benefit of a Roth individual retirement account is that, unlike traditional IRAs, withdrawals are tax-free when you reach age 59½. You can also withdraw any contributions, but not earnings, at any time regardless of your age.
In addition, IRAs typically offer a much wider variety of investment options than most 401 plans. Also, with a Roth IRA, you dont have to take required minimum distributions when you reach age 72.
You May Like: How Do I Get My 401k When I Retire
Pros And Cons Of A Roth Conversion
Your current income tax rate, your expected future tax rate, and the anticipated rate of return on your investments all factor into whether a conversion is a good, or bad, idea for you. These might not be easy determinations to make. Fortunately, there are many calculators available online to assist you.
The most critical issue might be whether you have the money available to pay the taxes that will come due. If you have to use any of the money you took out of your tax-deferred account to pay the taxes, this might be a strong indication that a Roth conversion might not be appropriate right now. Youre just giving the IRS a portion of your retirement savings before you have to.
-
Favors lower tax bracket early on
-
Major savings possible
-
Early tax hit can be detrimental to higher tax brackets
-
Funds must be reinvested to get the benefits
Where Should You Transfer Your 401
You have several options on what to do with your 401 savings after retirement or when you change jobs. For example, you can:
The right choice depends on your needs, and thats a choice everybody needs to make after evaluating all of the options.
Want help finding the right place for your retirement savings? Thats exactly what I do. As a fee-only fidicuary advisor, I can provide advice whether you prefer to pay a flat fee or youd like me to handle investment management for you, and I dont earn any commissions. To help with that decision, learn more about me or take a look at the Pricing page to see if it makes sense to talk. Theres no obligation to chat.
Important:The different rules that apply to 401 and IRA accounts are confusing. Discuss any transfers with a professional advisor before you make any decisions. This article is not tax advice, and you need to verify details with a CPA and your employers plan administrator. Likewise, only an attorney authorized to work in your state can provide guidance on legal matters. Approach Financial, Inc. does not provide tax or legal services. This information might not be applicable to your situation, it may be out of date, and it may contain errors and omissions.
Read Also: How To Transfer 401k To Vanguard Ira
You Want Lower Fees And More Investment Options
Because a 401 account is tied to an employer, it likely has a limited number of investment options, especially if the plan is administered by a small company.
For example, you might have access to only a small group of mutual funds with relatively high expense ratios, or fees. Many discount brokerages, on the other hand, offer index funds with expense ratios close to zero within self-directed IRA accounts.
In a 401, a lot of people feel like theyre handcuffed in terms of what they can own, says Hernandez. In most cases, in an IRA you have a lot more flexibility in what you can own.
Should You Convert To Roth
Hands holding piggy bank with Roth IRA. Pension plan.
Getty
Theres been a lot of talk about whether the backdoor Roth IRA and mega back door Roth conversions will be eliminated. However, this isnt the only reason to convert money to Roth. The most common reason is to pay taxes on pre-tax money now so the money can grow to be eventually tax-free. Lets take a look at some pros and cons, starting with reasons why now might not be the time for a Roth conversion:
1) The investments in the account have been doing very well. Considering that you have to pay ordinary income taxes in the tax year when you do the conversion, and the market tends to move in cycles, do you really want to pay taxes when your account balance is particularly high or when the value is eventually lower?
2) You have to withdraw money from the retirement account to pay the taxes. If you have to pay the taxes from money you withdraw from the account, it usually doesn’t make financial sense since that money will no longer be growing for your retirement. This is even more of a tax concern if the withdrawal is subject to a 10% early withdrawal penalty.
3) You’ll pay a lower tax rate in retirement. This can be a tricky one because the tendency is to compare your current tax bracket with what you expect it to be in retirement. There are a couple of things to keep in mind though.
Of course, there are also situations where a Roth conversion makes sense:
You May Like: How Much Income Will My 401k Generate
What Happens If I Take A Distribution From My Designated Roth Account Before The End Of The 5
If you take a distribution from your designated Roth account before the end of the 5-taxable-year period, it is a nonqualified distribution. You must include the earnings portion of the nonqualified distribution in gross income. However, the basis portion of the nonqualified distribution is not included in gross income. The basis portion of the distribution is determined by multiplying the amount of the nonqualified distribution by the ratio of designated Roth contributions to the total designated Roth account balance. For example, if a nonqualified distribution of $5,000 is made from your designated Roth account when the account consists of $9,400 of designated Roth contributions and $600 of earnings, the distribution consists of $4,700 of designated Roth contributions and $300 of earnings .
See Q& As regarding Rollovers of Designated Roth Contributions, for additional rules for rolling over both qualified and nonqualified distributions from designated Roth accounts.
Taxes May Derail Your Roth Ira Plans
When going from a traditional 401 to a Roth IRA, you need a tax plan. The amount you roll over into a Roth IRA will be counted as income.
Let’s say you convert $20,000 from your former employer’s 401 to a Roth IRA. The $20,000 will boost your gross income for the tax year, and will be taxed at your ordinary income rate. Your tax bill would be up to $4,400 on the conversion if your were 22%. But if the conversion bumps you into a higher tax bracket, you could end up owing more money.
Here are the ordinary income tax rates for each filing status that you need to consider if you convert your 401 to a Roth IRA in 2022:
|
Rate |
|---|
Recommended Reading: How To Borrow From 401k To Buy A House
Going From 401 To A Roth Ira
A 401 is one of the most popular vehicles used to feed retirement savings at work. It’s also a great way to slash your tax bill in the current year.
But if you leave your employer, you have to think about what you’re going to do with your 401. One option is to roll over your 401 to an IRA . You won’t have to worry about taxes yet if you choose a traditional IRA since it’s also a pre-tax account.
If you’re looking to get your tax tab out the way now, you may want to consider a Roth IRA. This is ideal if you expect your tax rate to be higher later. However, you’ll have to do some calculations to think about how going from a pre-tax account to an after-tax account will impact your current year tax bill.
Watch Your Money Grow Tax
Traditional IRAs force you to take required minimum distributions every year after you reach age 72 , regardless of whether you actually need the money. So you lose the tax-free growth on the money you had to withdraw.
On the other hand, Roth IRAs don’t have RMDs during your lifetime, so your money can stay in the account and keep growing tax-free.
Don’t Miss: Should I Contribute To Roth Or Traditional 401k
Since A Qualified Distribution From A Designated Roth Account Is Not Subject To Taxation Must The Distribution Be Reported
Yes, a distribution from a designated Roth account must be reported on Form 1099R, Distributions From Pensions, Annuities, Retirement or Profit-Sharing Plans, IRAs, Insurance Contracts, etc.PDF.
For direct rollovers, the plan administrator is required to provide the plan administrator of the plan accepting an eligible rollover distribution, with a statement indicating either the first year of the 5-taxable-year period for the employee and the portion of the distribution attributable to basis, or, that the distribution is a qualified distribution.
For other distributions, the plan administrator must provide to the employee, upon request, the portion of the distribution attributable to basis or that the distribution is a qualified distribution. The statement is required to be provided within a reasonable period following the employee request, but in no event later than 30 days following the employee request.
Sample Roth Conversion Ladder
Say youve contributed $50,000 to your Roth IRA to date. Youre 48 now, you plan to retire at age 53, and you want to withdraw $30,000 in each of the six years before you reach 59 ½ and can withdraw money penalty-free from your Roth IRA.
So, you need $180,000 in combined contributions and converted funds, but you only have $50,000. That makes you $130,000 short .
Because you want to start withdrawing money in five years, you should make your first conversion this year. For each of the next six years, you convert $21,667 from your workplace retirement account to your Roth IRA . You pay income taxes on this $21,667 each year.
In five years from now, at age 53, you can withdraw your first $30,000 from your Roth IRA tax- and penalty-free. That same year, youll continue to convert $21,667 from your traditional account to your Roth IRA, to cover your withdrawal at age 58.
Youll do the same thing the following year at age 54, but thats the last year youll have to convert funds. After that, the five year rule no longer matters, because at 59 ½ you can withdraw the money penalty-free anyway. From that age onward, you can just withdraw money without having to keep converting funds.
Recommended Reading: How To Find Out If Deceased Had 401k
How Many Times Can You Do A Roth Ira Conversion
You can convert any portion of a traditional IRA to a Roth IRA at any time. You are probably thinking of the once a year rollover rule. That rule applies to rollovers of traditional IRA money when the check is cut to the taxpayer and the taxpayer deposits the amount into another traditional IRA within 60 days.
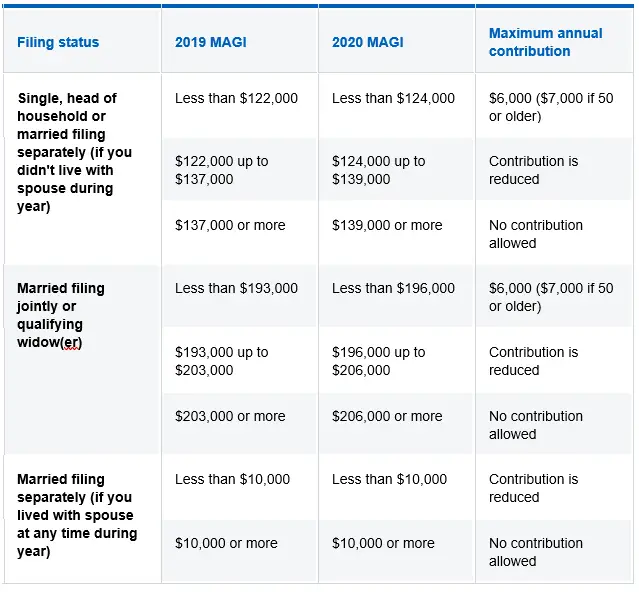
What Is The Income Limit For Roth Ira 2020
If you file taxes as a single person, your Modified Adjusted Gross Income must be under $139,000 for the tax year 2020 and under $140,000 for the tax year 2021 to contribute to a Roth IRA, and if you’re married and filing jointly, your MAGI must be under $206,000 for the tax year 2020 and $208,000 for the tax …
Also Check: How Much Are You Allowed To Contribute To 401k
Since I Make Designated Roth Contributions From After
No, the same restrictions on withdrawals that apply to pre-tax elective contributions also apply to designated Roth contributions. If your plan permits distributions from accounts because of hardship, you may choose to receive a hardship distribution from your designated Roth account. The hardship distribution will consist of a pro-rata share of earnings and basis and the earnings portion will be included in gross income unless you have had the designated Roth account for 5 years and are either disabled or over age 59 ½.
Should I Convert My 401 To A Roth Ira
Meet Joe Morgan and his daughter Samantha. Joe is 57 and Samantha just turned 27. Joe has worked for the same plastic manufacturing company for 35 years, first as a salesman and now as an executive. For decades, he has put money aside in his company’s 401 plan for retirement, and now it’s finally on the horizon.
Samantha graduated from medical school and just finished her residency. She’s starting her first high-paying job as a real doctor and is excited to put her student debt days behind her. Retirement seems far away, but she knows it’s never too early to start saving.
Both Joe and Samantha make more than $100,000 a year. Until 2010, only people who made less than $100,000 could convert a 401 retirement account into a Roth Investment Retirement Account , but those limits were lifted . Joe’s financial adviser thinks he should convert all of his 401 savings into a Roth IRA immediately, so Joe calls Samantha to see if she wants to do the same thing. But does a Roth IRA conversion make sense for both of them? And most importantly, does it make sense for you?
First, let’s define some terms. A 401 and a Roth IRA are two types of retirement savings accounts. In both cases, investors make contributions to the accounts while they are still working, and account managers invest those funds in a diverse portfolio of stocks, bonds, mutual funds and CDs. Ideally, the investments grow and the account holder has a nice nest egg to draw from during retirement.
Don’t Miss: Can I Rollover My 401k To A Money Market Account
Reasons Not To Convert From 401 To Roth Ira
Unlike her dad, 27-year-old Samantha Morgan doesn’t benefit from a lot of tax deductions. She’s single, with no dependents and renting a one-bedroom apartment. After years of struggling as a low-paid medical resident with lots of student loans, she is finally debt-free and earning a doctor’s salary, which puts her firmly in the 35 percent tax bracket.
One of the big reasons Joe Morgan decided to convert to a Roth IRA was because he expected to be in a higher tax bracket when he retired. Samantha, on the other hand, has good reason to expect to be earning considerably less, and paying less in taxes, after she retires. For that reason, it makes more sense for Samantha to make tax-free contributions to a 401, because she will pay a lower tax rate when she withdraws the 401 funds after retirement.
The other benefit of Samantha’s 401 is that her employer, St. Jude’s Hospital, matches a percentage of Samantha’s 401 contributions. That’s free money! The standard arrangement is to match 50 percent of employee 401 contributions every pay period up to the first 6 percent of salary . But if Samantha wants to maximize the match, she needs to pace herself.
The best advice is to talk to your tax professional about whether a 401 to Roth IRA conversion is right for you. For lots more information, check out the related HowStuffWorks links on the next page.
Can I Switch From 401k To Roth
Not every company allows employees to convert an existing 401 balance to a Roth 401. If you can’t convert, consider making your future 401 contributions to a Roth account rather than a traditional one. You are allowed to have both types. As mentioned, you’ll owe income tax on the amount you convert.
Read Also: What Is A 401k Profit Sharing Plan
Tips For Converting Your 401 Into A Roth Ira
Even if they wanted to, investors with larger 401 balances may not have the option of converting that entire amount in a given year, since doing so would create a substantial tax bill at years end. If you decide to roll over some of your pre-tax investments, select an amount that wont put you in a cold sweat. We highly recommend Roth conversions if it doesnt put a burden on your cash flow, says Pearson.
For those doing a partial conversion, prioritizing is key. Pearson recommends homing in on investments thats likely index or mutual funds for 401 holders that have taken the largest short-term hit in valuation. Withdrawing those funds will result in a lower tax liability come April 15 of next year. Should those investments shoot back up again, you wont have to worry about paying tax on those gains once you retire.
In addition, Pearson recommends choosing asset classes where youre going to see the biggest tax benefits. That means focusing on growth-oriented stock funds rather than bond funds, which dont have the same upside. Says Pearson: What youre trying to do is maximize your returns while minimizing the amount of tax youre going to pay.